Mutant prevention concentration as a measure of antibiotic potency: studies with clinical isolates of Mycobacterium tuberculosis
- PMID: 10952625
- PMCID: PMC90115
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.44.9.2581-2584.2000
Mutant prevention concentration as a measure of antibiotic potency: studies with clinical isolates of Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Abstract
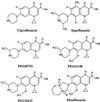
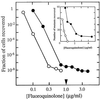
The mutant prevention concentration (MPC) of a C-8-methoxy fluoroquinolone exhibited a narrow distribution for 14 genetically diverse clinical isolates of Mycobacterium tuberculosis, indicating that results from single-isolate studies are likely to be representative. When one isolate was challenged with a variety of antituberculosis agents, C-8-methoxy fluoroquinolones were exceptional in having MPCs below the maximum concentration attained in serum by use of commonly recommended doses.
Figures

References
-
- Acocella G, Conti R, Luisetti M, Pozzi E, Grassi C. Pharmacokinetic studies on antituberculosis regimens in humans. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1985;132:510–515. - PubMed
-
- Acocella G, Nonis A, Perna G, Patane E, Gialdroni-Grassi G, Grassi C. Comparative bioavailability of isoniazid, rifampin, and pyrazinamide administered in free combination and in a fixed triple formulation designed for daily use in antituberculosis chemotherapy. II. Two-month, daily administration study. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1988;138:886–890. - PubMed
-
- Bifani P, Mathema B, Liu Z, Moghazeh S, Shopsin B, Tempalski B, Driscoll J, Frothingham R, Musser J, Alcabes P, Kreiswirth B. Identification of a W variant outbreak of Mycobacterium tuberculosis via population-based molecular epidemiology. JAMA. 1999;282:2321–2327. - PubMed
-
- Black H R, Griffith R S, Peabody A M. Absorption, excretion and metabolism of capreomycin in normal and diseased states. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1966;135:974–982. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

