Functions of E2A-HEB heterodimers in T-cell development revealed by a dominant negative mutation of HEB
- PMID: 10958665
- PMCID: PMC86175
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.20.18.6677-6685.2000
Functions of E2A-HEB heterodimers in T-cell development revealed by a dominant negative mutation of HEB
Abstract
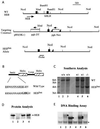
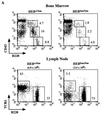
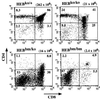
Lymphocyte development and differentiation are regulated by the basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) transcription factors encoded by the E2A and HEB genes. These bHLH proteins bind to E-box enhancers in the form of homodimers or heterodimers and, consequently, activate transcription of the target genes. E2A homodimers are the predominant bHLH proteins present in B-lineage cells and are shown genetically to play critical roles in B-cell development. E2A-HEB heterodimers, the major bHLH dimers found in thymocyte extracts, are thought to play a similar role in T-cell development. However, disruption of either the E2A or HEB gene led to only partial blocks in T-cell development. The exact role of E2A-HEB heterodimers and possibly the E2A and HEB homodimers in T-cell development cannot be distinguished in simple disruption analysis due to a functional compensation from the residual bHLH homodimers. To further define the function of E2A-HEB heterodimers, we generated and analyzed a dominant negative allele of HEB, which produces a physiological amount of HEB proteins capable of forming nonfunctional heterodimers with E2A proteins. Mice carrying this mutation show a stronger and earlier block in T-cell development than HEB complete knockout mice. The developmental block is specific to the alpha/beta T-cell lineage at a stage before the completion of V(D)J recombination at the TCRbeta gene locus. This defect is intrinsic to the T-cell lineage and cannot be rescued by expression of a functional T-cell receptor transgene. These results indicate that E2A-HEB heterodimers play obligatory roles both before and after TCRbeta gene rearrangement during the alpha/beta lineage T-cell development.
Figures
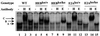




References
-
- Bain G, Maandag E C, Izon D J, Amsen D, Kruisbeek A M, Weintraub B C, Krop I, Schlissel M S, Feeney A J, van Roon M, van der Valk M, te Riele H P J, Berns A, Murre C. E2A proteins are required for proper B cell development and initiation of immunoglobulin gene rearrangements. Cell. 1994;79:885–892. - PubMed
-
- Bain G, Maandag E C R, te Riele H P, Feeney A J, Sheehy A, Schlissel M, Shinton S A, Hardy R R, Murre C. Both E12 and E47 allow commitment to the B cell lineage. Immunity. 1997;6:145–154. - PubMed
-
- Barndt R J, Dai M F, Zhuang Y. A novel role for HEB downstream or parallel to the pre-TCR signal during alpha/beta thymopoiesis. J Immunology. 1999;163:3331–3343. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
