YM-53601, a novel squalene synthase inhibitor, reduces plasma cholesterol and triglyceride levels in several animal species
- PMID: 10960070
- PMCID: PMC1572301
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0703545
YM-53601, a novel squalene synthase inhibitor, reduces plasma cholesterol and triglyceride levels in several animal species
Abstract
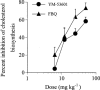
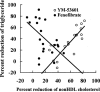
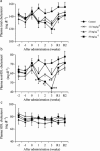
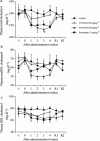
The aim of this study was to evaluate the potency of YM-53601 ((E)-2-[2-fluoro-2-(quinuclidin-3-ylidene) ethoxy]-9H-carbazole monohydrochloride), a new inhibitor of squalene synthase, in reducing both plasma cholesterol and triglyceride levels, compared with 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) reductase inhibitor and fibrates, respectively. YM-53601 equally inhibited squalene synthase activities in hepatic microsomes prepared from several animal species and also suppressed cholesterol biosynthesis in rats (ED(50), 32 mg kg(-1)). In guinea-pigs, YM-53601 and pravastatin reduced plasma nonHDL-C (=total cholesterol - high density lipoprotein cholesterol) by 47% (P<0.001) and 33% (P<0.001), respectively (100 mg kg(-1), daily for 14 days). In rhesus monkeys, YM-53601 decreased plasma nonHDL-C by 37% (50 mg kg(-1), twice daily for 21 days, P<0.01), whereas the HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor, pravastatin, failed to do (25 mg kg(-1), twice daily for 28 days). YM-53601 caused plasma triglyceride reduction in hamsters fed a normal diet (81% decrease at 50 mg kg(-1), daily for 5 days, P<0.001). In hamsters fed a high-fat diet, the ability of YM-53601 to lower triglyceride (by 73%, P<0.001) was superior to that of fenofibrate (by 53%, P<0.001), the most potent fibrate (dosage of each drug: 100 mg kg(-1), daily for 7 days). This is the first report that a squalene synthase inhibitor is superior to an HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor in lowering plasma nonHDL-C level in rhesus monkeys and is superior to a fibrate in significantly lowering plasma triglyceride level. YM-53601 may therefore prove useful in treating hypercholesterolemia and hypertriglyceridemia in humans.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Experimental model of escape phenomenon in hamsters and the effectiveness of YM-53601 in the model.Br J Pharmacol. 2002 Mar;135(6):1572-8. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0704595. Br J Pharmacol. 2002. PMID: 11906972 Free PMC article.
-
YM-53601, a novel squalene synthase inhibitor, suppresses lipogenic biosynthesis and lipid secretion in rodents.Br J Pharmacol. 2003 May;139(1):140-6. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705229. Br J Pharmacol. 2003. PMID: 12746232 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of YM-53601, a novel squalene synthase inhibitor, on the clearance rate of plasma LDL and VLDL in hamsters.Br J Pharmacol. 2002 Oct;137(4):561-9. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0704906. Br J Pharmacol. 2002. PMID: 12359639 Free PMC article.
-
Squalene synthase: a critical enzyme in the cholesterol biosynthesis pathway.Clin Genet. 2009 Jan;75(1):19-29. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.2008.01099.x. Epub 2008 Nov 27. Clin Genet. 2009. PMID: 19054015 Review.
-
Squalene synthase inhibitors : clinical pharmacology and cholesterol-lowering potential.Drugs. 2007;67(1):11-6. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200767010-00002. Drugs. 2007. PMID: 17209661 Review.
Cited by
-
Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of WC-9 analogs as antiparasitic agents.Eur J Med Chem. 2013 Nov;69:480-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2013.09.009. Epub 2013 Sep 18. Eur J Med Chem. 2013. PMID: 24090919 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of cholesterologenesis by the oxysterol receptor, LXRalpha.J Biol Chem. 2008 Sep 26;283(39):26332-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M804808200. Epub 2008 Aug 1. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18676367 Free PMC article.
-
Differential Regulation of Gene Expression by Cholesterol Biosynthesis Inhibitors That Reduce (Pravastatin) or Enhance (Squalestatin 1) Nonsterol Isoprenoid Levels in Primary Cultured Mouse and Rat Hepatocytes.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2016 Aug;358(2):216-29. doi: 10.1124/jpet.116.233312. Epub 2016 May 25. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2016. PMID: 27225895 Free PMC article.
-
Small Molecule Regulators of Ferroptosis.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021;1301:81-121. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-62026-4_6. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021. PMID: 34370289
-
Identification of non-conventional small molecule degraders and stabilizers of squalene synthase.Chem Sci. 2023 Oct 18;14(45):12973-12983. doi: 10.1039/d3sc04064j. eCollection 2023 Nov 22. Chem Sci. 2023. PMID: 38023519 Free PMC article.
References
-
- AMIN D., CORNELL S.A., GUSTAFSON S.K., NEEDLE S.J., ULLRICH J.W., BILDER G.E., PERRONE M.H. Bisphosphonates used for the treatment of bone disorders inhibit squalene synthase and cholesterol biosynthesis. J. Lipid Res. 1992;33:1657–1663. - PubMed
-
- AMIN D., RUTLEDGE R.Z., NEEDLE S.N., GALCZENSKI H.F., NEUENSCHWANDER K., SCOTESE A.C., MAGUIRE M.P., BUSH R.C., HELE D.J., BILDER G.E., PERRONE M.H. RPR 107393, a potent squalene synthase inhibitor and orally effective cholesterol-lowering agent: comparison with inhibitors of HMG-CoA reductase. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1997;281:746–752. - PubMed
-
- AMIN D., RUTLEDGE R.Z., NEEDLE S.J., HELE D.J., NEUENSWANDER K., BUSH R.C., BILDER G.E., PERRONE M.H. RPR 101821, a new potent cholesterol-lowering agent: inhibition of squalene synthase and 7-dehydrocholesterol reductase. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 1996;353:233–240. - PubMed
-
- BERGSTROM J.D., DUFRESNE C., BILLS G.F., NALLIN-OMSTEAD M., BYRNE K. Discovery, biosynthesis, and mechanism of action of the zaragozic acids: potent inhibitors of squalene synthase. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 1995;49:607–639. - PubMed
-
- CIOSEK C.P., JR, MAGNIN D.R., HARRITY T.W., LOGAN J.V.H., DICKSON J.K., JR, GORDON E.M., HAMILTON K.A., JOLIBOIS K.G., KUNSELMAN L.K., LAWRENCE R.M., MOOKHTIAR K.A., RICH L.C., SLUSARCHYK D.A., SULSKY R.B., BILLER S.A. Lipophilic 1,1-bisphosphonates are potent squalene synthase inhibitors and orally active cholesterol lowering agents in vivo. J. Biol. Chem. 1993;268:24832–24837. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

