Mechanisms of the thapsigargin-induced Ca(2+) entry in in situ endothelial cells of the porcine aortic valve and the endothelium-dependent relaxation in the porcine coronary artery
- PMID: 10960077
- PMCID: PMC1572304
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0703548
Mechanisms of the thapsigargin-induced Ca(2+) entry in in situ endothelial cells of the porcine aortic valve and the endothelium-dependent relaxation in the porcine coronary artery
Abstract
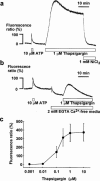
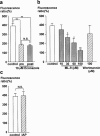
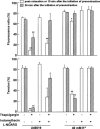
The mechanisms of the thapsigargin (TG)-induced capacitative Ca(2+) entry in in situ endothelial cells and its role in the regulation of arterial tone were investigated using front-surface fluorimetry and fura-2-loaded strips of porcine aortic valve and coronary artery. In the presence of extracellular Ca(2+), TG induced an initial rapid and a subsequent sustained elevation of cytosolic Ca(2+) concentration ([Ca(2+)](i)) in valvular strips. In the absence of extracellular Ca(2+), TG induced only a transient increase in [Ca(2+)](i). The TG-induced sustained elevation of [Ca(2+)](i) in endothelial cells was inhibited completely by 1 mM Ni(2+) and partly by 10 microM econazole and 30 microM ML-9, but not by 900 ng ml(-1) pertussis toxin or 100 microM wortmannin. Therefore, cytochrome P450 and protein phosphorylation are suggested to be involved in the TG-induced Ca(2+) influx in in situ endothelial cells. TG induced an endothelium-dependent large relaxation consisting of an initial and a late sustained relaxation in coronary arterial strip precontracted with U46619 (a thromboxane A2 analogue). Indomethacin alone had no effect, while indomethacin plus N(omega)-nitro-L-arginine (L-NOARG) markedly inhibited the sustained phase and slightly inhibited the initial phase of the TG-induced relaxation. TG induced a smaller but sustained relaxation during the 40 mM K(+)-induced precontraction than that seen during the U46619-induced precontraction. This relaxation was completely abolished by the pretreatment with indomethacin plus L-NOARG. In conclusion, both nitric oxide (NO) and endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factor were suggested to mediate the TG-induced relaxation, while NO plays a major role in the sustained relaxation. The TG-induced sustained [Ca(2+)](i) elevation in endothelial cells was thus suggested to be mainly linked to the sustained production of NO.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Mechanism of trypsin-induced endothelium-dependent vasorelaxation in the porcine coronary artery.Br J Pharmacol. 2001 Oct;134(4):815-26. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0704318. Br J Pharmacol. 2001. PMID: 11606322 Free PMC article.
-
Motilin induces the endothelium-dependent relaxation of smooth muscle and the elevation of cytosolic calcium in endothelial cells in situ.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994 Jul 15;202(1):346-53. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1994.1934. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994. PMID: 8037731
-
Inhibitory effects of brefeldin A, a membrane transport blocker, on the bradykinin-induced hyperpolarization-mediated relaxation in the porcine coronary artery.Br J Pharmacol. 2001 Sep;134(1):168-78. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0704246. Br J Pharmacol. 2001. PMID: 11522609 Free PMC article.
-
Nitric oxide- and nitric oxide donor-induced relaxation.Methods Enzymol. 1996;269:107-19. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(96)69013-2. Methods Enzymol. 1996. PMID: 8791641 Review. No abstract available.
-
From isolated vessels to the catheterization laboratory. Studies of endothelial function in the coronary circulation of humans.Circulation. 1989 Sep;80(3):703-6. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.80.3.703. Circulation. 1989. PMID: 2670317 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Pharmacological profile of store-operated channels in cerebral arteriolar smooth muscle cells.Br J Pharmacol. 2003 Jul;139(5):955-65. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705327. Br J Pharmacol. 2003. PMID: 12839869 Free PMC article.
-
Myosin light chain kinase-independent inhibition by ML-9 of murine TRPC6 channels expressed in HEK293 cells.Br J Pharmacol. 2007 Sep;152(1):122-31. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0707368. Epub 2007 Jul 2. Br J Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17603544 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of calcium channels in smooth muscle: new insights into the role of myosin light chain kinase.Channels (Austin). 2014;8(5):402-13. doi: 10.4161/19336950.2014.950537. Channels (Austin). 2014. PMID: 25483583 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- ALVAREZ J., MONTERO M., GARCIA-SANCHO J. Cytochrome P450 may regulate plasma membrane Ca2+ permeability according to the filling state of the intracellular Ca2+ stores. FASEB J. 1992;6:786–792. - PubMed
-
- AOKI H., KOBAYASHI S., NISHIMURA J., YAMAMOTO H., KANAIDE H. Endothelin induces the Ca2+-transient in endothelial cells in situ. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1991;181:1352–1357. - PubMed
-
- BIRD G.S., PUTNEY J.W.J. Inhibition of thapsigargin-induced calcium entry by microinjected guanine nucleotide analogues. Evidence for the involvement of a small G-protein in capacitative calcium entry. J. Biol. Chem. 1993;268:21486–21488. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

