Enhanced reduction of myocardial infarct size by combined ACE inhibition and AT(1)-receptor antagonism
- PMID: 10960080
- PMCID: PMC1572300
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0703544
Enhanced reduction of myocardial infarct size by combined ACE inhibition and AT(1)-receptor antagonism
Abstract
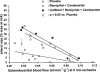
The effects of the angiotensin-converting-enzyme inhibitor (ACEI) ramiprilat, the angiotensin II type 1 receptor antagonist (AT(1)A) candesartan, and the combination of both drugs on infarct size (IS) resulting from regional myocardial ischaemia were studied in pigs. Both ACEI and AT(1)A reduce myocardial IS by a bradykinin-mediated process. It is unclear, however, whether the combination of ACEI and AT(1)A produces a more pronounced IS reduction than each of these drugs alone. Forty-six enflurane-anaesthetized pigs underwent 90 min low-flow ischaemia and 120 min reperfusion. Systemic haemodynamics (micromanometer), subendocardial blood flow (ENDO, microspheres) and IS (TTC-staining) were determined. The decreases in left ventricular peak pressure by ACEI (by 9+/-2 (s.e. mean) mmHg), AT(1)A (by 11+/-2 mmHg) or their combination (by 18+/-3 mmHg, P<0.05 vs ACEI and AT(1)A, respectively) were readjusted by aortic constriction prior to ischaemia. With placebo (n=10), IS averaged 20.0+/-3.3% of the area at risk. IS was reduced to 9.8+/-2.6% with ramiprilat (n=10) and 10.6+/-3.1% with candesartan (n=10). Combined ramiprilat and candesartan (n=10) reduced IS to 6.7+/-2.1%. Blockade of the bradykinin-B(2)-receptor with icatibant prior to ACEI and AT(1)A completely abolished the reduction of IS (n=6, 22.8+/-6.1%). The relationship between IS and ischaemic ENDO with placebo was shifted downwards by each ACEI and AT(1)A and further shifted downwards with their combination (P<0.05 vs all groups); icatibant again abolished such downward shift. The combination of ACEI and AT(1)A enhances the reduction of IS following ischaemia/reperfusion compared to a monotherapy by either drug alone; this effect is mediated by bradykinin.
Figures
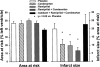

References
-
- ACUTE INFARCTION RAMIPRIL EFFICACY (AIRE) INVESTIGATORS (THE) Effect of ramipril on mortality and morbidity of survivors of acute myocardial infarction with clinical evidence of heart failure. Lancet. 1993;342:821–828. - PubMed
-
- AZIZI M., CHATELLIER G., GUYENE T.-T., MURIETA-GEOFFROY D., MÉNARD J. Additive effects of combined angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition and angiotensin II antagonism on blood pressure and renin release in sodium-depleted normotensives. Circulation. 1995;92:825–834. - PubMed
-
- BARUCH L., ANAND I., COHEN I.S., ZIESCHE S., JUDD D., COHN J.N. Augmented short- and long-term hemodynamic and hormonal effects of an angiotensin receptor blocker added to angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor therapy in patients with heart failure. Circulation. 1999;99:2658–2664. - PubMed
-
- BLACK S.C., GRALINSKI M.R., MCCORMACK J.G., DRISCOLL E.M., LUCCHESI B.R. Effect of ranolazine on infarct size in a canine model of regional myocardial ischemia/reperfusion. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 1994;24:921–928. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

