Formation of 8-iso-PGF(2alpha) and thromboxane A(2) by stimulation with several activators of phospholipase A(2) in the isolated human umbilical vein
- PMID: 10960081
- PMCID: PMC1572303
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0703547
Formation of 8-iso-PGF(2alpha) and thromboxane A(2) by stimulation with several activators of phospholipase A(2) in the isolated human umbilical vein
Abstract
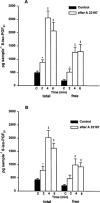
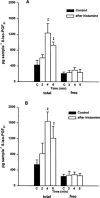
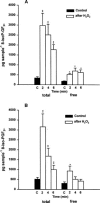
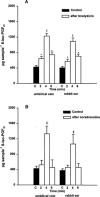
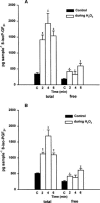
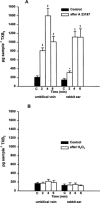
We investigated the effects of the phospholipase A(2) (PLA(2)) activators calcium ionophore A 23187, hydrogen peroxide (H(2)O(2)), bradykinin (BK), histamine and noradrenaline (NA) on the 8-iso-prostaglandin (PG)F(2alpha) formation in the isolated human umbilical vein and the isolated rabbit ear. For comparison, the influence of these substances on the thromboxane A(2) (TXA(2)) release was also investigated. The release of total (esterified as well as free) 8-iso-PGF(2alpha), free 8-iso-PGF(2alpha) and TXB(2), the stable metabolite of TXA(2), was determined by specific enzyme immunoassays. The results show that bolus injections of 5.4 mmol H(2)O(2), 30 nmol A 23187, 10 nmol BK, 50 nmol histamine and 20 nmol NA caused an increased release of total 8-iso-PGF(2alpha) in the umbilical vein and the rabbit ear. A perfusion with H(2)O(2) at a final concentration of 0.3 mM also increased the release of this isoprostane. Increased formation of free 8-iso-PGF(2alpha) was induced by A 23187 injection and by both modes of H(2)O(2) administration, but not by the other treatments. Bolus injections of A 23187, BK and histamine induced an increased release of TXB(2) in both organs. Both modes of H(2)O(2) administration and NA showed no releasing effects. In conclusion, our results show that the substances used are able to stimulate the formation of 8-iso-PGF(2alpha) concurrently with the release of PGs. This effect might be of pathophysiological relevance in inflammatory and cardiovascular diseases in which an enhanced release of free radicals, BK, histamine or NA play an important role.
Figures

References
-
- BENBAREK H., MOUITHYS-MICKALAD A., DEBY-DUPONT G., DEBY C., GRÜLKE S., NEMMAR A., LAMY M., SERTEYN D. High concentrations of histamine stimulate equine polymorphonuclear neutrophils to produce reactive oxygen species. Inflamm. Res. 1999;48:594–601. - PubMed
-
- BINGHAM C.O., AUSTEN K.F. Phospholipase A2 enzymes in eicosanoid generation. Proc. Ass. Am. Physicans. 1999;111:516–524. - PubMed
-
- CHEROUNY P.H., GHODGAONKAR R.B., NIEBYL J.R., DUBIN N.H. Effect of hydrogen peroxide on prostaglandin production and contractions of the pregnant rat uterus. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 1988;159:1390–1394. - PubMed
-
- CIRINO G. Multiple controls in inflammation. Extracellular and intracellular phospholipase A2 inducible and constitutive cyclooxygenase, and inducible nitric oxide synthase. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1998;55:105–111. - PubMed
-
- DAVI G., ALESSANDRINI P., MEZZETTI A., MINOTTI G., BUCCIARELLI T., CONSTANTINI F., CIPOLLONE F., BON G.B., CIABATTONI G., PATRONO C. In vivo formation of 8-epi-prostaglandin F2α in hypercholesterolemia. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 1997;17:3230–3235. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

