Recovery of hydrogen peroxide-sensitive culturable cells of Vibrio vulnificus gives the appearance of resuscitation from a viable but nonculturable state
- PMID: 10960089
- PMCID: PMC94653
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.182.18.5070-5075.2000
Recovery of hydrogen peroxide-sensitive culturable cells of Vibrio vulnificus gives the appearance of resuscitation from a viable but nonculturable state
Abstract
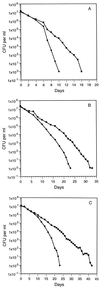
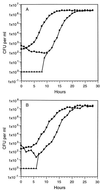
The viabilities of five strains of Vibrio vulnificus were evaluated during the storage of the organisms in sterile seawater at 5 degrees C. The number of CFU was measured by plate count methods on rich media. The total cell numbers were determined by direct microscopic count methods. The titer of CFU declined logarithmically to undetectable levels over a period of 2 to 3 weeks, while the total cell numbers were unchanged. Midway through each study, higher culturable cell counts began to be observed on plates containing catalase or sodium pyruvate; during the latter stages of the study, the plate counts on such media were up to 1,000-fold higher than those on unsupplemented plates. Because autoclaving is known to generate hydrogen peroxide in rich media, and because catalase and sodium pyruvate are known to eliminate hydrogen peroxide, it appears that the conditions of the experiments led to the selection of a hydrogen peroxide-sensitive culturable cell subpopulation. At the time of the final stage of the decline in viability of each culture, hydrogen peroxide-sensitive cells were the only culturable cells present. Warming samples of the cultures to room temperature led to the growth of these residual culturable cells, utilizing nutrients provided by the nonculturable cells. The cells that grew recovered hydrogen peroxide resistance. When mixtures of culturable and nonculturable cells were diluted to the point where only nonculturable cells were present, or when the hydrogen peroxide-sensitive culturable cells had declined to undetectable levels, warming had no effect; no culturable cells were recovered. Warming has been reported to "resuscitate" nonculturable cells. Recognition of the existence of hydrogen peroxide-sensitive culturable cell populations, as well as their ability to grow to high levels in the warmed seawater microcosms, leads instead to the conclusion that while warming permits culturable cells to grow, it has no effect on nonculturable cells.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Resuscitation of Vibrio vulnificus from the viable but nonculturable state.J Bacteriol. 1991 Aug;173(16):5054-9. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.16.5054-5059.1991. J Bacteriol. 1991. PMID: 1860818 Free PMC article.
-
Temperature-induced recovery of Vibrio cholerae from the viable but nonculturable state: growth or resuscitation?Microbiology (Reading). 1995 Feb;141 ( Pt 2):377-83. doi: 10.1099/13500872-141-2-377. Microbiology (Reading). 1995. PMID: 7704268
-
Stress resistance and recovery potential of culturable and viable but nonculturable cells of Vibrio vulnificus.Microbiology (Reading). 1996 Apr;142 ( Pt 4):845-853. doi: 10.1099/00221287-142-4-845. Microbiology (Reading). 1996. PMID: 8936311
-
Vibrio vulnificus: a physiological and genetic approach to the viable but nonculturable response.J Infect Chemother. 2000 Jun;6(2):115-20. doi: 10.1007/pl00012150. J Infect Chemother. 2000. PMID: 11810549 Review.
-
The viable but non-culturable state in the human pathogen Vibrio vulnificus.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1995 Nov 15;133(3):203-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1995.tb07885.x. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1995. PMID: 8522135 Review.
Cited by
-
Reaching unreachables: Obstacles and successes of microbial cultivation and their reasons.Front Microbiol. 2023 Mar 7;14:1089630. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1089630. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 36960281 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Differential growth response of colony-forming alpha- and gamma-proteobacteria in dilution culture and nutrient addition experiments from Lake Kinneret (Israel), the eastern Mediterranean Sea, and the Gulf of Eilat.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2003 Jan;69(1):199-211. doi: 10.1128/AEM.69.1.199-211.2003. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2003. PMID: 12513996 Free PMC article.
-
Generation of Distinct Differentially Culturable Forms of Burkholderia following Starvation at Low Temperature.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Feb 23;10(1):e0211021. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.02110-21. Epub 2022 Jan 5. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 34985335 Free PMC article.
-
Inactivation of the regulatory gene algU or gacA can affect the ability of biocontrol Pseudomonas fluorescens CHA0 to persist as culturable cells in nonsterile soil.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2002 Apr;68(4):2085-8. doi: 10.1128/AEM.68.4.2085-2088.2002. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2002. PMID: 11916739 Free PMC article.
-
Validation of a green fluorescent protein-labeled strain of Vibrio vulnificus for use in the evaluation of postharvest strategies for handling of raw oysters.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2006 Nov;72(11):7205-11. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01091-06. Epub 2006 Sep 15. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2006. PMID: 16980431 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barer M R, Gribbon L T, Harwood C R, Nwoguh C E. The viable but non-culturable hypothesis and medical bacteriology. Rev Med Microbiol. 1993;4:183–191.
-
- Barer M R, Harwood C R. Bacterial viability and culturability. Adv Microb Physiol. 1999;41:93–137. - PubMed
-
- Barry V C, Conalty M L, Denneny J M, Winder F. Peroxide formation in bacteriological media. Nature. 1956;178:596–597. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

