A RUNX2/PEBP2alpha A/CBFA1 mutation displaying impaired transactivation and Smad interaction in cleidocranial dysplasia
- PMID: 10962029
- PMCID: PMC27062
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.180309597
A RUNX2/PEBP2alpha A/CBFA1 mutation displaying impaired transactivation and Smad interaction in cleidocranial dysplasia
Abstract
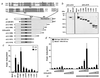
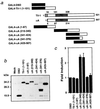
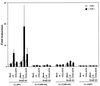
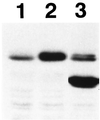
Cleidocranial dysplasia (CCD), an autosomal-dominant human bone disease, is thought to be caused by heterozygous mutations in runt-related gene 2 (RUNX2)/polyomavirus enhancer binding protein 2alphaA (PEBP2alphaA)/core-binding factor A1 (CBFA1). To understand the mechanism underlying the pathogenesis of CCD, we studied a novel mutant of RUNX2, CCDalphaA376, originally identified in a CCD patient. The nonsense mutation, which resulted in a truncated RUNX2 protein, severely impaired RUNX2 transactivation activity. We show that signal transducers of transforming growth factor beta superfamily receptors, Smads, interact with RUNX2 in vivo and in vitro and enhance the transactivation ability of this factor. The truncated RUNX2 protein failed to interact with and respond to Smads and was unable to induce the osteoblast-like phenotype in C2C12 myoblasts on stimulation by bone morphogenetic protein. Therefore, the pathogenesis of CCD may be related to the impaired Smad signaling of transforming growth factor beta/bone morphogenetic protein pathways that target the activity of RUNX2 during bone formation.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A RUNX2/PEBP2alphaA/CBFA1 mutation in cleidocranial dysplasia revealing the link between the gene and Smad.J Bone Miner Metab. 2001;19(3):188-94. doi: 10.1007/s007740170041. J Bone Miner Metab. 2001. PMID: 11368305
-
Mutations in the RUNX2 gene in patients with cleidocranial dysplasia.Hum Mutat. 2002 Mar;19(3):209-16. doi: 10.1002/humu.10043. Hum Mutat. 2002. PMID: 11857736 Review.
-
Delayed tooth eruption and suppressed osteoclast number in the eruption pathway of heterozygous Runx2/Cbfa1 knockout mice.Arch Oral Biol. 2004 Jun;49(6):435-42. doi: 10.1016/j.archoralbio.2004.01.010. Arch Oral Biol. 2004. PMID: 15099800
-
Cleidocranial dysplasia with severe parietal bone dysplasia: C-terminal RUNX2 mutations.Birth Defects Res A Clin Mol Teratol. 2006 Feb;76(2):78-85. doi: 10.1002/bdra.20231. Birth Defects Res A Clin Mol Teratol. 2006. PMID: 16463420 Review.
-
Core-binding factor beta interacts with Runx2 and is required for skeletal development.Nat Genet. 2002 Dec;32(4):633-8. doi: 10.1038/ng1015. Epub 2002 Nov 18. Nat Genet. 2002. PMID: 12434152
Cited by
-
Role of the Interaction of Tumor Necrosis Factor-α and Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptors 1 and 2 in Bone-Related Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jan 27;23(3):1481. doi: 10.3390/ijms23031481. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35163403 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mitotic retention of gene expression patterns by the cell fate-determining transcription factor Runx2.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 Feb 27;104(9):3189-94. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0611419104. Epub 2007 Feb 20. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007. PMID: 17360627 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of TGF-beta signaling and its roles in progression of tumors.Cancer Sci. 2003 Mar;94(3):230-4. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2003.tb01425.x. Cancer Sci. 2003. PMID: 12824914 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Stimulation of bone formation and prevention of bone loss by prostaglandin E EP4 receptor activation.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002 Apr 2;99(7):4580-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.062053399. Epub 2002 Mar 26. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002. PMID: 11917107 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear microenvironments support physiological control of gene expression.Chromosome Res. 2003;11(5):527-36. doi: 10.1023/a:1024943214431. Chromosome Res. 2003. PMID: 12971727 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

