Subcellular localization of wild-type and Parkinson's disease-associated mutant alpha -synuclein in human and transgenic mouse brain
- PMID: 10964942
- PMCID: PMC6772969
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.20-17-06365.2000
Subcellular localization of wild-type and Parkinson's disease-associated mutant alpha -synuclein in human and transgenic mouse brain
Abstract
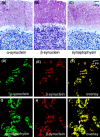
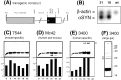
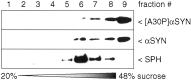
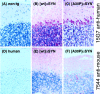
Mutations in the alpha-synuclein (alphaSYN) gene are associated with rare cases of familial Parkinson's disease, and alphaSYN is a major component of Lewy bodies and Lewy neurites. Here we have investigated the localization of wild-type and mutant [A30P]alphaSYN as well as betaSYN at the cellular and subcellular level. Our direct comparative study demonstrates extensive synaptic colocalization of alphaSYN and betaSYN in human and mouse brain. In a sucrose gradient equilibrium centrifugation assay, a portion of betaSYN floated into lower density fractions, which also contained the synaptic vesicle marker synaptophysin. Likewise, wild-type and [A30P]alphaSYN were found in floating fractions. Subcellular fractionation of mouse brain revealed that both alphaSYN and betaSYN were present in synaptosomes. In contrast to synaptophysin, betaSYN and alphaSYN were recovered from the soluble fraction upon lysis of the synaptosomes. Synaptic colocalization of alphaSYN and betaSYN was directly visualized by confocal microscopy of double-stained human brain sections. The Parkinson's disease-associated human mutant [A30P]alphaSYN was found to colocalize with betaSYN and synaptophysin in synapses of transgenic mouse brain. However, in addition to their normal presynaptic localization, transgenic wild-type and [A30P]alphaSYN abnormally accumulated in neuronal cell bodies and neurites throughout the brain. Thus, mutant [A30P]alphaSYN does not fail to be transported to synapses, but its transgenic overexpression apparently leads to abnormal cellular accumulations.
Figures


References
-
- Abeliovich A, Schmitz Y, Fariñas I, Choi-Lundberg D, Ho W-H, Castillo PE, Shinsky N, Garcia Verdugo JM, Armanini M, Ryan A, Hynes M, Phillips H, Sulzer D, Rosenthal A. Mice lacking α-synuclein display functional deficits in the nigrostriatal dopamine system. Neuron. 2000;25:239–252. - PubMed
-
- Arawaka S, Saito Y, Murayama S, Mori H. Lewy body in neurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation type 1 is immunoreactive for α-synuclein. Neurology. 1998;51:887–889. - PubMed
-
- Arima K, Uéda K, Sunohara N, Hirai S, Izumiyama Y, Tonozuka-Uehara H, Kawai M. Immunoelectron-microscopic demonstration of NACP/α-synuclein-epitopes on the filamentous component of Lewy bodies in Parkinson's disease and in dementia with Lewy bodies. Brain Res. 1998;808:93–100. - PubMed
-
- Conway KA, Harper JD, Lansbury PT. Accelerated in vitro fibril formation by a mutant α-synuclein linked to early-onset Parkinson disease. Nat Med. 1998;4:1318–1320. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
