Eph receptors and ephrins in the developing chick cerebellum: relationship to sagittal patterning and granule cell migration
- PMID: 10964955
- PMCID: PMC6772988
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.20-17-06488.2000
Eph receptors and ephrins in the developing chick cerebellum: relationship to sagittal patterning and granule cell migration
Abstract
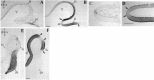
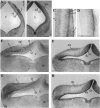
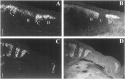
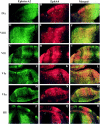
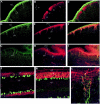
Spatiotemporal expression patterns of six members of the Eph gene family (EphA4, EphA3, EphB2, ephrin-B1, ephrin-A2, and ephrin-A5) were characterized immunocytochemically at various stages of chick cerebellar development. EphA4 expression is observed in the cerebellar anlage as early as embryonic day 5 (E5) and continues in the posthatch cerebellum. During the early period of cerebellar development (E3-E8), complementarity is observed between EphA4 and ephrin-A5 expression within the cerebellar-isthmal region. By E8, differential expression of EphA4 in parasagittal Purkinje cell bands is evident, and the expression remains banded in the posthatch cerebellum. Banded expression of the ephrin-A5 ligand complements EphA4 expression during the middle period (E9-E15). During this period, ephrin-A2 and EphA3 are coexpressed in a banded pattern and with variable correlation to EphA4. Variability in the banding expression is observed for EphA4, EphA3, ephrin-A5, and ephrin-A2 across different lobes, and graded complementarity in the expression pattern of EphA3 and ephrin-A5 is observed in the external granular layer between the posterior and anterior lobes. Analysis of Purkinje cell birth date in correlation with Eph-ephrin expression during the middle period reveals that early-born cells express EphA4, whereas late-born cells express ephrin-A5. Finally, EphA4 expression domains are respected by migrating granule cell ribbons, which express both ephrin-B1 and EphB2. These expression patterns suggest multiple roles for the Eph-ephrin system in cerebellar development, including demarcation/enforcement of boundaries of the cerebellar anlage, formation/maintenance of Purkinje cell compartments, and restriction of the early phase of granule cell migration to ribbons.
Figures





References
-
- Altman J, Bayer SA. Atlas of prenatal rat brain development. CRC; Boca Raton, FL: 1995.
-
- Alvarez Otero R, Sotelo C, Alvarado-Mallart RM. Chick/quail chimeras with partial cerebellar grafts: an analysis of the origin and migration of cerebellar cells. J Comp Neurol. 1993;333:597–615. - PubMed
-
- Arndt K, Redies C. Development of cadherin-defined parasagittal subdivisions in the embryonic chicken cerebellum. J Comp Neurol. 1998;401:367–381. - PubMed
-
- Arndt K, Nakagawa S, Takeichi M, Redies C. Cadherin-defined segments and parasagittal cell ribbons in the developing chicken cerebellum. Mol Cell Neurosci. 1998;10:211–228. - PubMed
-
- Baader SL, Schilling ML, Rosengarten B, Pretsch W, Teutsch HF, Oberdick J, Schilling K. Purkinje cell lineage and the topographic organization of the cerebellar cortex: a view from X inactivation mosaics. Dev Biol. 1996;174:393–406. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
