Hydrogen peroxide sensitivity of catechol-2,3-dioxygenase: a cautionary note on use of xylE reporter fusions under aerobic conditions
- PMID: 10966438
- PMCID: PMC92268
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.66.9.4119-4123.2000
Hydrogen peroxide sensitivity of catechol-2,3-dioxygenase: a cautionary note on use of xylE reporter fusions under aerobic conditions
Abstract
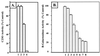
Catechol-2,3-dioxygenase (C23O) of Pseudomonas putida, encoded by the xylE gene, was found to be sensitive to hydrogen peroxide (H(2)O(2)) when used as a reporter in gene fusion constructs. Exposure of Pseudomonas aeruginosa katA or katA katB mutants harboring katA- or katB-lacZ (encoding beta-galactosidase) or -xylE fusion plasmids to H(2)O(2) stimulated beta-galactosidase activity, while there was little or no detectable C23O activity in these strains. More than 95% of C23O activity was lost after a 5-min exposure to equimolar H(2)O(2), while a 10,000-fold excess was required for similar inhibition of beta-galactosidase. Electron paramagnetic resonance spectra of the nitrosyl complexes of C23O showed that H(2)O(2) nearly stoichiometrically oxidized the essential active-site ferrous ion, thus accounting for the loss of activity. Our results suggest using caution in interpreting data derived from xylE reporter fusions under aerobic conditions, especially where oxidative stress is present or when catalase-deficient strains are used.
Figures
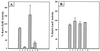


References
-
- Aasa R, Vänngård T. EPR signal intensity and powder shapes: a re-examination. J Magn Reson. 1975;19:308–315.
-
- Arciero D M, Lipscomb J D. Binding of 17O-labeled substrate and inhibitors to protocatechuate 4,5-dioxygenase-nitrosyl complex. Evidence for direct substrate binding to the active site Fe2+ of extradiol dioxygenases. J Biol Chem. 1986;261:2170–2178. - PubMed
-
- Arciero D M, Lipscomb J D, Huynh B H, Kent T A, Munck E. EPR and Mossbauer studies of protocatechuate 4,5-dioxygenase. Characterization of a new Fe2+ environment. J Biol Chem. 1983;258:14981–14991. - PubMed
-
- Arciero D M, Orville A M, Lipscomb J D. [17O]water and nitric oxide binding by protocatechuate 4,5-dioxygenase and catechol 2,3-dioxygenase. Evidence for binding of exogenous ligands to the active site Fe2+ of extradiol dioxygenases. J Biol Chem. 1985;260:14035–14044. - PubMed
-
- Brown C A, Pavlosky M A, Westre T E, Zhang Y, Hedman B, Hodgson K O, Solomon E I. Spectroscopic and theoretical description of the electronic structure of S=3/2 iron-nitrosyl complexes and their relation to O2 activation by non-heme iron enzyme active sites. J Am Chem Soc. 1995;117:715–732.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

