Comparison of St John's wort and imipramine for treating depression: randomised controlled trial
- PMID: 10968813
- PMCID: PMC27467
- DOI: 10.1136/bmj.321.7260.536
Comparison of St John's wort and imipramine for treating depression: randomised controlled trial
Abstract
Objectives: To compare the efficacy and tolerability of Hypericum perforatum (St John's wort extract) with imipramine in patients with mild to moderate depression.
Design: Randomised, multicentre, double blind, parallel group trial.
Setting: 40 outpatient clinics in Germany.
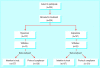
Participants: 324 outpatients with mild to moderate depression.
Intervention: 75 mg imipramine twice daily or 250 mg hypericum extract ZE 117 twice daily for 6 weeks.
Main outcome measures: Hamilton depression rating scale, clinical global impression scale, and patient's global impression scale.
Results: Among the 157 participants taking hypericum mean scores on the Hamilton depression scale decreased from 22.4 at baseline to 12.00 at end point; among the 167 participants taking imipramine they fell from 22.1 to 12.75. Mean clinical global impression scores at end point were 2.22 out of 7 for the hypericum group and 2.42 for the imipramine group. On the 7 point self assessments of global improvement completed by participants (score of 1 indicating "very much improved" and 7 indicating "very much deteriorated") mean scores were 2.44 in the hypericum group and 2.60 in the imipramine group. None of the differences between treatment groups were significant. However, the mean score on the anxiety-somatisation subscale of the Hamilton scale (3.79 in the hypericum group and 4.26 in the imipramine group) indicated a significant advantage for hypericum relative to imipramine. Mean scores on the 5 point scale used by participants to assess tolerability (score of 1 indicating excellent tolerability and 5 indicating very poor tolerability) were better for hypericum (1.67) than imipramine (2.35). Adverse events occurred in 62/157 (39%) participants taking hypericum and in 105/167 (63%) taking imipramine. 4 (3%) participants taking hypericum withdrew because of adverse events compared with 26 (16%) taking imipramine.
Conclusions: This Hypericum perforatum extract is therapeutically equivalent to imipramine in treating mild to moderate depression, but patients tolerate hypericum better.
Figures
Comment in
-
Comparison of St John's Wort and imipramine. Remission is important outcome.BMJ. 2001 Feb 24;322(7284):493; author reply 494. BMJ. 2001. PMID: 11222430 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Comparison of St John's Wort and imipramine. Study design casts doubt on value of St John's wort in treating depression.BMJ. 2001 Feb 24;322(7284):493; author reply 494. BMJ. 2001. PMID: 11222432 No abstract available.
-
Comparison of St John's Wort and imipramine. Finding must be treated with caution.BMJ. 2001 Feb 24;322(7284):493; author reply 494. BMJ. 2001. PMID: 11222434 No abstract available.
-
Comparison of St John's Wort and imipramine. Sensitivity of assay is questionable.BMJ. 2001 Feb 24;322(7284):493-4. BMJ. 2001. PMID: 11256367 No abstract available.
-
Antidepressant trials generally have methodological defects.BMJ. 2001 Sep 8;323(7312):574. doi: 10.1136/bmj.323.7312.574. BMJ. 2001. PMID: 11573492 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Fernie WT. Herbal simples. Bristol: John Wright; 1897.
-
- Pratt A. Wild flowers. London: Society for Promoting Christian Knowledge; 1853.
-
- Pickering C. Chronological history of plants. Boston: Little Brown; 1879.
-
- Commission Nationale de Pharmacopée France. Pharmacopée française. 10th ed. Paris: Adrapharm; 1982.
-
- Kommission Deutscher Arzneimittel-Codex. Johanniskraut—Hyperici herba. DAC; 1986.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical