Genotyping of the capsule gene cluster (cps) in nontypeable group B streptococci reveals two major cps allelic variants of serotypes III and VII
- PMID: 10970395
- PMCID: PMC87398
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.38.9.3420-3428.2000
Genotyping of the capsule gene cluster (cps) in nontypeable group B streptococci reveals two major cps allelic variants of serotypes III and VII
Abstract
Forty group B Streptococcus (GBS) isolates obtained from Europe and the United States previously reported to be nontypeable (NT) by capsule serotype determination were subjected to buoyant density gradient centrifugation. From nearly half of the isolates capsule-expressing variants could be selected. For characterization of the remaining NT-GBS isolates, the capsule operon (cps) was amplified by the long-fragment PCR technique and compared by restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) analysis. The patterns from serotype reference isolates (n = 32) were first determined and used as a comparison matrix for the NT-GBS isolates. Using two restriction enzymes, SduI and AvaII, cluster analysis revealed a high degree of similarity within serotypes but less than 88% similarity between serotypes. However, serotypes III and VII were each split in two distant RFLP clusters, which were designated III(1) and III(2) and VII(1) and VII(2), respectively. Among the isolates that remained NT after repeated Percoll gradient selections, two insertional mutants were revealed. Both were found in blood isolates and harbored insertion sequence (IS) elements within cpsD: one harbored IS1548, and the other harbored IS861. All other NT-GBS isolates could, by cluster analysis, be referred to different serotypes by comparison to the RFLP reference matrix. In pulsed-field gel electrophoresis of SmaI-restricted chromosomal DNA, patterns from allelic type 1 and 2 isolates were essentially distributed in separate clusters in serotypes III and VII. A covariation with insertion sequence IS1548 in the hylB gene was suggested for serotype III, since allelic type III(1) harboring IS1548 in hylB, clustered separately. The variation in serotype VII was not dependent on the presence of IS1548, which was not detected at any position in the type VII chromosome.
Figures

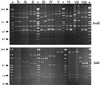

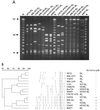
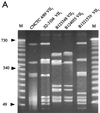



References
-
- Arbeit R D. Laboratory procedures for the epidemiologic analysis of microorganisms. In: Murray P R, Baron E J, Pfaller M A, Tenover F C, Yolken R H, editors. Manual of clinical microbiology. 7th ed. Washington, D.C.: American Society for Microbiology; 1999. pp. 116–137.
-
- Baker C J, Edwards M S. Group B streptococcal infections. In: Remington J S, Klein J S, editors. Infectious diseases of the fetus and newborn infant. 4th ed. Philadelphia, Pa: W. B. Saunders Co.; 1995. pp. 980–1028.
-
- Blumberg H M, Stephens D S, Modansky M, Erwin M, Elliot J, Facklam R R, Schuchat A, Baughman W, Farley M M. Invasive group B streptococcal disease: the emergence of serotype V. J Infect Dis. 1996;173:365–373. - PubMed
-
- Dillon H C, Jr, Gray E, Pass M A, Gray B M. Anorectal and vaginal carriage of group B streptococci during pregnancy. J Infect Dis. 1982;145:794–799. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

