Mixed infection caused by two species of Fusarium in a human immunodeficiency virus-positive patient
- PMID: 10970404
- PMCID: PMC87407
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.38.9.3460-3462.2000
Mixed infection caused by two species of Fusarium in a human immunodeficiency virus-positive patient
Abstract
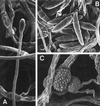
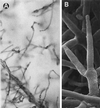
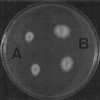
We report on a case of mixed infection caused by two species of Fusarium in a human immunodeficiency virus-positive patient with lymphoma who was neutropenic due to chemotherapy. The patient showed the typical signs of a disseminated fusarial infection, with Fusarium solani isolated from skin lesions and F. verticillioides isolated from blood. The report discusses how difficult it is to make an accurate diagnosis when an immunosuppressed patient is infected with more than one fungal species, especially when the species are morphologically very similar.
Figures
References
-
- Boutati E I, Anaissie E J. Fusarium, a significant emerging pathogen in patients with hematologic malignancy: ten years' experience at a cancer center and implications for management. Blood. 1997;90:999–1008. - PubMed
-
- Cribier B, Mena M L, Rey D, Partisani M, Fabien V, Lang J M, Grosshans E. Nail changes in patients infected with human immunodeficiency virus. A prospective controlled study. Arch Dermatol. 1998;134:1216–1220. - PubMed
-
- Glasgow B J, Engstrom R F, Jr, Holland G N, Kreiger A E, Wool M G. Bilateral endogenous Fusarium endophthalmitis associated with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Arch Ophthalmol. 1996;114:873–875. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

