Degradation of Drosophila PIM regulates sister chromatid separation during mitosis
- PMID: 10970883
- PMCID: PMC316890
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.176700
Degradation of Drosophila PIM regulates sister chromatid separation during mitosis
Abstract
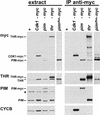
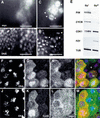
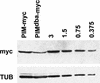
Drosophila Pimples (PIM) and Three rows (THR) are required for sister chromatid separation in mitosis. PIM accumulates during interphase and is degraded rapidly during mitosis. This degradation is dependent on a destruction box similar to that of B-type cyclins. Nondegradable PIM with a mutant destruction box can rescue sister chromatid separation in pim mutants but only when expressed at low levels. Higher levels of nondegradable PIM, as well as overexpression of wild-type PIM, inhibit sister chromatid separation. Moreover, cells arrested in mitosis before sister chromatid separation (by colcemid or by mutations in fizzy/CDC20) fail to degrade PIM. Thus, although not related by primary sequence, PIM has intriguing functional similarities to the securin proteins of budding yeast, fission yeast, and vertebrates. Whereas these securins are known to form a complex with separins, we show that PIM associates in vivo with THR, which does not contain the conserved separin domain.
Figures




References
-
- Blat Y, Kleckner N. Cohesins bind to preferential sites along yeast chromosome III, with differential regulation along arms versus the centric region. Cell. 1999;98:249–259. - PubMed
-
- Brand AH, Perrimon N. Targeted gene expression as a means of altering cell fates and generating dominant phenotypes. Development. 1993;118:401–415. - PubMed
-
- Chen RH, Waters JC, Salmon ED, Murray AW. Association of spindle assembly checkpoint component XMAD2 with unattached kinetochores. Science. 1996;274:242–246. - PubMed
-
- Ciosk R, Zachariae W, Michaelis C, Shevchenko A, Mann M, Nasmyth K. An ESP1/PDS1 complex regulates loss of sister chromatid cohesion at the metaphase to anaphase transition in yeast. Cell. 1998;93:1067–1076. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
