Resistance/susceptibility to Echinococcus multilocularis infection and cytokine profile in humans. II. Influence of the HLA B8, DR3, DQ2 haplotype
- PMID: 10971516
- PMCID: PMC1905739
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.2000.01309.x
Resistance/susceptibility to Echinococcus multilocularis infection and cytokine profile in humans. II. Influence of the HLA B8, DR3, DQ2 haplotype
Abstract
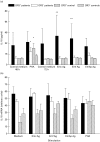
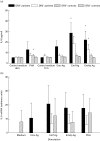
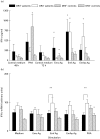
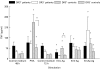
Differences have been shown between HLA characteristics of patients with different courses of alveolar echinococcosis (AE). Notably the HLA B8, DR3, DQ2 haplotype was associated with more severe forms of this granulomatous parasitic disease. We compared IL-10, IL-5, interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma) and tumour necrosis factor (TNF) secretion by peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) isolated from eight HLA-DR3+, DQ2+, B8+ AE patients and from 10 HLA-DR3-, DQ2-, B8- patients after non-specific mitogenic and specific Echinococcus multilocularis antigenic in vitro stimulation. PBMC from seven HLA-DR3+, DQ2+, B8+ healthy subjects and nine HLA-DR3-, DQ2-, B8- subjects were also studied as controls. PBMC from AE patients with HLA DR3+, DQ2+ haplotype secreted higher levels of IL-10 without any stimulation and after specific antigenic stimulation than did patients without this haplotype. Higher levels of IL-5 and IFN-gamma were also produced by these patients' PBMC after stimulation with non-purified parasitic antigenic preparations; however, the specific alkaline phosphatase antigen extracted from E. multilocularis induced only Th2-type cytokine secretion. A spontaneous secretion of TNF by HLA DR3+, DQ2+ B8+ AE patients was also found. These results suggest that HLA characteristics of the host can influence immune-mediated mechanisms, and thus the course of AE in humans; specific antigenic components of E. multilocularis could contribute to the preferential Th2-type cytokine production favoured by the genetic background of the host.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Resistance/susceptibility to Echinococcus multilocularis infection and cytokine profile in humans. I. Comparison of patients with progressive and abortive lesions.Clin Exp Immunol. 2000 Sep;121(3):484-90. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.2000.01308.x. Clin Exp Immunol. 2000. PMID: 10971515 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro cytokine production by HLA-B8,DR3 positive subjects.Autoimmunity. 1994;18(2):121-32. doi: 10.3109/08916939409007985. Autoimmunity. 1994. PMID: 7742473
-
Profile of cytokine production within the periparasitic granuloma in human alveolar echinococcosis.Acta Trop. 2003 Feb;85(2):231-6. doi: 10.1016/s0001-706x(02)00218-8. Acta Trop. 2003. PMID: 12606101
-
Modification of cytokine patterns in subjects bearing the HLA-B8,DR3 phenotype: implications for autoimmunity.Cytokines Cell Mol Ther. 1997 Dec;3(4):217-24. Cytokines Cell Mol Ther. 1997. PMID: 9740350 Review.
-
The genetic basis for the association of the 8.1 ancestral haplotype (A1, B8, DR3) with multiple immunopathological diseases.Immunol Rev. 1999 Feb;167:257-74. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1999.tb01398.x. Immunol Rev. 1999. PMID: 10319267 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular characterization of antigen B2 subunit in two genotypes of Echinococcus granulosus from Indian bubaline isolates, its stage specific expression and serological evaluation.Mol Biol Rep. 2011 Mar;38(3):2067-73. doi: 10.1007/s11033-010-0332-7. Epub 2010 Sep 18. Mol Biol Rep. 2011. PMID: 20852940
-
Components of the mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade are activated in hepatic cells by Echinococcus multilocularis metacestode.World J Gastroenterol. 2009 May 7;15(17):2116-24. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.2116. World J Gastroenterol. 2009. PMID: 19418584 Free PMC article.
-
Echinococcus metacestode: in search of viability markers.Parasite. 2014;21:63. doi: 10.1051/parasite/2014063. Epub 2014 Nov 28. Parasite. 2014. PMID: 25429386 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hepatic echinococcosis: clinical and therapeutic aspects.World J Gastroenterol. 2012 Apr 7;18(13):1448-58. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i13.1448. World J Gastroenterol. 2012. PMID: 22509076 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Major histocompatibility complex class II DAB alleles associated with intestinal parasite load in the vulnerable Chinese egret (Egretta eulophotes).Ecol Evol. 2016 Jun 7;6(13):4421-34. doi: 10.1002/ece3.2226. eCollection 2016 Jul. Ecol Evol. 2016. PMID: 27386085 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Miguet JP, Bresson-Hadni S, Vuitton DA. Echinococcosis of the liver. In: McIntyre B, Benhamou JP, Bircher J, Rizetto M, Rodes J, editors. Oxford textbook of clinical hepatology. Oxford: Oxford University Press; 1991. p. 721.
-
- Godot V, Harraga S, Deschaseaux M, et al. Increased basal production of interleukin-10 by peripheral blood mononuclear cells in human alveolar echinococcosis. Eur Cytokine Netw. 1997;8:401–8. - PubMed
-
- Emery I, Liance M, Deriaud E, et al. Characterization of T-cell immune response of Echinococcus multilocularis-infected C57BL/6J mice. Parasite Immunol. 1996;18:1–10. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

