The ER repeat protein YT521-B localizes to a novel subnuclear compartment
- PMID: 10973987
- PMCID: PMC2175241
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.150.5.949
The ER repeat protein YT521-B localizes to a novel subnuclear compartment
Abstract
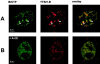
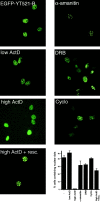
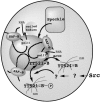
The characterization of distinct subnuclear domains suggests a dynamic nuclear framework supporting gene expression and DNA replication. Here, we show that the glutamic acid/arginine-rich domain protein YT521-B localizes to a novel subnuclear structure, the YT bodies. YT bodies are dynamic compartments, which first appear at the beginning of S-phase in the cell cycle and disperse during mitosis. Furthermore, in untreated cells of the human cell line MCF7 they were undetectable and appeared only after drug- induced differentiation. YT bodies contain transcriptionally active sites and are in close contact to other subnuclear structures such as speckles and coiled bodies. YT bodies disperse upon actinomycin D treatment, whereas other transcriptional inhibitors such as alpha-amanitin or DRB have little effect. On the basis of our experiments, we propose that YT521-B may participate in the assembly of genes into transcription centers, thereby allowing efficient regulation of gene expression.
Figures



Similar articles
-
An RNA recognition motif (RRM) is required for the localization of PTB-associated splicing factor (PSF) to subnuclear speckles.Exp Cell Res. 2001 Feb 1;263(1):131-44. doi: 10.1006/excr.2000.5097. Exp Cell Res. 2001. PMID: 11161712
-
The intranuclear localization and function of YT521-B is regulated by tyrosine phosphorylation.Hum Mol Genet. 2004 Aug 1;13(15):1535-49. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddh167. Epub 2004 Jun 2. Hum Mol Genet. 2004. PMID: 15175272
-
Paraspeckles: a novel nuclear domain.Curr Biol. 2002 Jan 8;12(1):13-25. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(01)00632-7. Curr Biol. 2002. PMID: 11790299
-
Nuclear speckles: a model for nuclear organelles.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2003 Aug;4(8):605-12. doi: 10.1038/nrm1172. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2003. PMID: 12923522 Review.
-
Targeting and association of proteins with functional domains in the nucleus: the insoluble solution.Int Rev Cytol. 1995;162B:303-35. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)62620-0. Int Rev Cytol. 1995. PMID: 8557490 Review.
Cited by
-
Nuclear speckles.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2011 Feb 1;3(2):a000646. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a000646. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2011. PMID: 20926517 Free PMC article. Review.
-
YTHDC1 promotes postnatal brown adipose tissue development and thermogenesis by stabilizing PPARγ.EMBO J. 2025 Jun;44(12):3360-3380. doi: 10.1038/s44318-025-00460-x. Epub 2025 May 12. EMBO J. 2025. PMID: 40355558 Free PMC article.
-
N6-Methyladenosine on mRNA facilitates a phase-separated nuclear body that suppresses myeloid leukemic differentiation.Cancer Cell. 2021 Jul 12;39(7):958-972.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2021.04.017. Epub 2021 May 27. Cancer Cell. 2021. PMID: 34048709 Free PMC article.
-
Biochemical and structural basis for YTH domain of human YTHDC1 binding to methylated adenine in DNA.Nucleic Acids Res. 2020 Oct 9;48(18):10329-10341. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaa604. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020. PMID: 32663306 Free PMC article.
-
Validation of reference genes for quantitative RT-PCR studies of gene expression in perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne L.).BMC Mol Biol. 2010 Jan 20;11:8. doi: 10.1186/1471-2199-11-8. BMC Mol Biol. 2010. PMID: 20089196 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alblas J., Slager-Davidov R., Steenbergh P.H., Sussenbach J.S., van der Burg B. The role of MAP kinase in TPA-mediated cell cycle arrest of human breast cancer cells. Oncogene. 1998;16:131–139. - PubMed
-
- Ashraf S.I., Ip Y.T. Transcriptional controlrepression by local chromatin modification. Curr. Biol. 1998;8:R683–R686. - PubMed
-
- Assier E., Bouzinba-Segard H., Stolzenberg M.-C., Stephens R., Bardos J., Freemont P., Charron D., Trowsdale J., Rich T. Isolation, sequencing and expression of RED, a novel human gene encoding anacidic-basic dipeptide repeat. Gene. 1999;230:145–154. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

