The ER repeat protein YT521-B localizes to a novel subnuclear compartment
- PMID: 10973987
- PMCID: PMC2175241
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.150.5.949
The ER repeat protein YT521-B localizes to a novel subnuclear compartment
Abstract
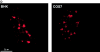
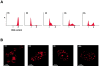
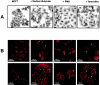
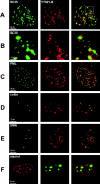
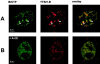
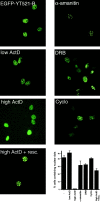
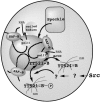
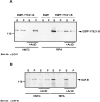
The characterization of distinct subnuclear domains suggests a dynamic nuclear framework supporting gene expression and DNA replication. Here, we show that the glutamic acid/arginine-rich domain protein YT521-B localizes to a novel subnuclear structure, the YT bodies. YT bodies are dynamic compartments, which first appear at the beginning of S-phase in the cell cycle and disperse during mitosis. Furthermore, in untreated cells of the human cell line MCF7 they were undetectable and appeared only after drug- induced differentiation. YT bodies contain transcriptionally active sites and are in close contact to other subnuclear structures such as speckles and coiled bodies. YT bodies disperse upon actinomycin D treatment, whereas other transcriptional inhibitors such as alpha-amanitin or DRB have little effect. On the basis of our experiments, we propose that YT521-B may participate in the assembly of genes into transcription centers, thereby allowing efficient regulation of gene expression.
Figures



References
-
- Alblas J., Slager-Davidov R., Steenbergh P.H., Sussenbach J.S., van der Burg B. The role of MAP kinase in TPA-mediated cell cycle arrest of human breast cancer cells. Oncogene. 1998;16:131–139. - PubMed
-
- Ashraf S.I., Ip Y.T. Transcriptional controlrepression by local chromatin modification. Curr. Biol. 1998;8:R683–R686. - PubMed
-
- Assier E., Bouzinba-Segard H., Stolzenberg M.-C., Stephens R., Bardos J., Freemont P., Charron D., Trowsdale J., Rich T. Isolation, sequencing and expression of RED, a novel human gene encoding anacidic-basic dipeptide repeat. Gene. 1999;230:145–154. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

