Preservation of mitochondrial structure and function after Bid- or Bax-mediated cytochrome c release
- PMID: 10973993
- PMCID: PMC2175243
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.150.5.1027
Preservation of mitochondrial structure and function after Bid- or Bax-mediated cytochrome c release
Abstract
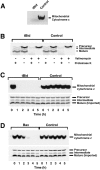
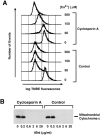
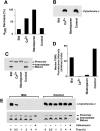
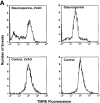
Proapoptotic members of the Bcl-2 protein family, including Bid and Bax, can activate apoptosis by directly interacting with mitochondria to cause cytochrome c translocation from the intermembrane space into the cytoplasm, thereby triggering Apaf-1-mediated caspase activation. Under some circumstances, when caspase activation is blocked, cells can recover from cytochrome c translocation; this suggests that apoptotic mitochondria may not always suffer catastrophic damage arising from the process of cytochrome c release. We now show that recombinant Bid and Bax cause complete cytochrome c loss from isolated mitochondria in vitro, but preserve the ultrastructure and protein import function of mitochondria, which depend on inner membrane polarization. We also demonstrate that, if caspases are inhibited, mitochondrial protein import function is retained in UV-irradiated or staurosporine-treated cells, despite the complete translocation of cytochrome c. Thus, Bid and Bax act only on the outer membrane, and lesions in the inner membrane occurring during apoptosis are shown to be secondary caspase-dependent events.
Figures




References
-
- Cecconi F., Alvarez-Bolado G., Meyer B.I., Roth K.A., Gruss P. Apaf1 (CED-4 homolog) regulates programmed cell death in mammalian development. Cell. 1998;94:727–737. - PubMed
-
- Chautan M., Chazal G., Cecconi F., Gruss P., Golstein P. Interdigital cell death can occur through a necrotic and caspase-independent pathway. Curr. Biol. 1999;9:967–970. - PubMed
-
- Deshmukh M., Johnson E.M., Jr. Evidence of a novel event during neuronal deathdevelopment of competence-to-die in response to cytoplasmic cytochrome c. Neuron. 1998;21:695–705. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

