Regulation of programmed cell death by basement membranes in embryonic development
- PMID: 10974008
- PMCID: PMC2175256
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.150.5.1215
Regulation of programmed cell death by basement membranes in embryonic development
Abstract
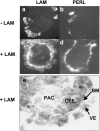
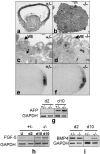
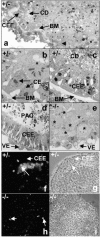
The formation of the proamniotic cavity in the mammalian embryo is the earliest of many instances throughout development in which programmed cell death and the formation of epithelia play fundamental roles (Coucouvanis, E., and G.R. Martin. 1995. Cell. 83:279-287). To determine the role of the basement membrane (BM) in cavitation, we use embryoid bodies derived from mouse embryonic stem cells in which the LAMC1 genes have been inactivated to prevent BM deposition (Smyth, N., H.S. Vatansever, P. Murray, M. Meyer, C. Frie, M. Paulsson, and D. Edgar. 1999. J. Cell Biol. 144:151-610). We demonstrate here that LAMC1-/- embryoid bodies are unable to cavitate, and do not form an epiblast epithelium in the absence of a BM, although both embryonic ectodermal cells and extraembryonic endodermal cells do differentiate, as evidenced by the expression of cell-specific markers. Acceleration or rescue of BM deposition by exogenous laminin in wild-type or LAMC1-/- embryoid bodies, respectively, results in cavitation that is temporally and spatially associated with restoration of epiblast epithelial development. We conclude that the BM not only directly regulates development of epiblast epithelial cells, but also indirectly regulates the programmed cell death necessary for cavity formation.
Figures
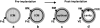
References
-
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal. Biochem. 1987;162:156–159. - PubMed
-
- Coles H.S., Burne J.F., Raff M.C. Large-scale normal cell death in the developing rat kidney and its reduction by epidermal growth factor. Development. 1993;118:777–784. - PubMed
-
- Coucouvanis E., Martin G.R. Signals for death and survivala two-step mechanism for cavitation in the vertebrate embryo. Cell. 1995;83:279–287. - PubMed
-
- Coucouvanis E., Martin G.R. BMP signaling plays a role in visceral endoderm differentiation and cavitation in the early mouse embryo. Development. 1999;126:535–546. - PubMed
-
- Dziadek M., Adamson E. Localization and synthesis of alphafoetoprotein in post-implantation mouse embryos. J. Embryol. Exp. Morphol. 1978;43:289–313. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

