Analysis of Qa-1(b) peptide binding specificity and the capacity of CD94/NKG2A to discriminate between Qa-1-peptide complexes
- PMID: 10974028
- PMCID: PMC2193274
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.192.5.613
Analysis of Qa-1(b) peptide binding specificity and the capacity of CD94/NKG2A to discriminate between Qa-1-peptide complexes
Abstract
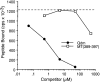
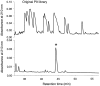
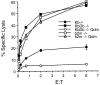
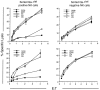
The major histocompatibility complex class Ib protein, Qa-1(b), serves as a ligand for murine CD94/NKG2A natural killer (NK) cell inhibitory receptors. The Qa-1(b) peptide-binding site is predominantly occupied by a single nonameric peptide, Qa-1 determinant modifier (Qdm), derived from the leader sequence of H-2D and L molecules. Five anchor residues were identified in this study by measuring the peptide-binding affinities of substituted Qdm peptides in experiments with purified recombinant Qa-1(b). A candidate peptide-binding motif was determined by sequence analysis of peptides eluted from Qa-1 that had been folded in the presence of random peptide libraries or pools of Qdm derivatives randomized at specific anchor positions. The results indicate that Qa-1(b) can bind a diverse repertoire of peptides but that Qdm has an optimal primary structure for binding Qa-1(b). Flow cytometry experiments with Qa-1(b) tetramers and NK target cell lysis assays demonstrated that CD94/NKG2A discriminates between Qa-1(b) complexes containing peptides with substitutions at nonanchor positions P4, P5, or P8. Our findings suggest that it may be difficult for viruses to generate decoy peptides that mimic Qdm and raise the possibility that competitive replacement of Qdm with other peptides may provide a novel mechanism for activation of NK cells.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The nonclassical MHC class I molecule Qa-1 forms unstable peptide complexes.J Immunol. 2004 Feb 1;172(3):1661-9. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.172.3.1661. J Immunol. 2004. PMID: 14734748
-
Analysis of HLA-E peptide-binding specificity and contact residues in bound peptide required for recognition by CD94/NKG2.J Immunol. 2003 Aug 1;171(3):1369-75. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.171.3.1369. J Immunol. 2003. PMID: 12874227
-
Functional analysis of the molecular factors controlling Qa1-mediated protection of target cells from NK lysis.J Immunol. 2001 Feb 1;166(3):1601-10. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.166.3.1601. J Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11160201
-
Qa-1, a nonclassical class I histocompatibility molecule with roles in innate and adaptive immunity.Immunol Res. 2004;29(1-3):81-92. doi: 10.1385/IR:29:1-3:081. Immunol Res. 2004. PMID: 15181272 Review.
-
Natural killer cell surveillance of intracellular antigen processing pathways mediated by recognition of HLA-E and Qa-1b by CD94/NKG2 receptors.Microbes Infect. 2000 Apr;2(4):371-80. doi: 10.1016/s1286-4579(00)00330-0. Microbes Infect. 2000. PMID: 10817639 Review.
Cited by
-
ERAAP Shapes the Peptidome Associated with Classical and Nonclassical MHC Class I Molecules.J Immunol. 2016 Aug 15;197(4):1035-43. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1500654. Epub 2016 Jul 1. J Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27371725 Free PMC article.
-
Stress signals activate natural killer cells.J Exp Med. 2002 Dec 2;196(11):1399-402. doi: 10.1084/jem.20021747. J Exp Med. 2002. PMID: 12461075 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Expression profiling of major histocompatibility and natural killer complex genes reveals candidates for controlling risk of graft versus host disease.PLoS One. 2011 Jan 28;6(1):e16582. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0016582. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21305040 Free PMC article.
-
Implications of CD94 deficiency and monoallelic NKG2A expression for natural killer cell development and repertoire formation.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002 Jan 22;99(2):868-73. doi: 10.1073/pnas.022500599. Epub 2002 Jan 8. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002. PMID: 11782535 Free PMC article.
-
Differential expression of inhibitory receptor NKG2A distinguishes disease-specific exhausted CD8+ T cells.MedComm (2020). 2022 Jan 10;3(1):e111. doi: 10.1002/mco2.111. eCollection 2022 Mar. MedComm (2020). 2022. PMID: 35281793 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Stanton T.H., Boyse E.A. A new serologically defined locus, Qa-1, in the Tla-region of the mouse. Immunogenetics. 1976;3:525–531.
-
- Lalanne J.L., Transy C., Guerin S., Darche S., Meulien P., Kourilsky P. Expression of class I genes in the major histocompatibility complexidentification of eight distinct mRNAs in DBA/2 mouse liver. Cell. 1985;41:469–478. - PubMed
-
- Fischer Lindahl K. Unrestricted killer cells recognize an antigen controlled by a gene linked to Tla. Immunogenetics. 1979;8:71–77.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

