Akt-dependent cytokine production in mast cells
- PMID: 10974038
- PMCID: PMC2193272
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.192.5.729
Akt-dependent cytokine production in mast cells
Abstract
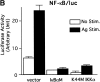
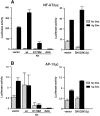
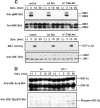
Cross-linking of FcepsilonRI induces the activation of three protein tyrosine kinases, Lyn, Syk, and Bruton's tyrosine kinase (Btk), leading to the secretion of a panel of proinflammatory mediators from mast cells. This study showed phosphorylation at Ser-473 and enzymatic activation of Akt/protein kinase B, the crucial survival kinase, upon FcepsilonRI stimulation in mouse mast cells. Phosphorylation of Akt is regulated positively by Btk and Syk and negatively by Lyn. Akt in turn can regulate positively the transcriptional activity of interleukin (IL)-2 and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha promoters. Transcription from the nuclear factor kappaB (NF-kappaB), nuclear factor of activated T cells (NF-AT), and activator protein 1 (AP-1) sites within these promoters is under the control of Akt activity. Accordingly, the signaling pathway involving IkappaB-alpha, a cytoplasmic protein that binds NF-kappaB and inhibits its nuclear translocation, appears to be regulated by Akt in mast cells. Catalytic activity of glycogen synthase kinase (GSK)-3beta, a serine/threonine kinase that phosphorylates NF-AT and promotes its nuclear export, seems to be inhibited by Akt. Importantly, Akt regulates the production and secretion of IL-2 and TNF-alpha in FcepsilonRI-stimulated mast cells. Altogether, these results revealed a novel function of Akt in transcriptional activation of cytokine genes via NF-kappaB, NF-AT, and AP-1 that contributes to the production of cytokines.
Figures




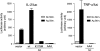



Similar articles
-
Role of activator protein 1, nuclear factor-kappaB, and nuclear factor of activated T cells in IgE receptor-mediated cytokine expression in mature human mast cells.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2003 May;111(5):1062-8. doi: 10.1067/mai.2003.1342. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2003. PMID: 12743571
-
Bruton's tyrosine kinase-mediated interleukin-2 gene activation in mast cells. Dependence on the c-Jun N-terminal kinase activation pathway.J Biol Chem. 1998 May 1;273(18):10979-87. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.18.10979. J Biol Chem. 1998. PMID: 9556577
-
The B cell antigen receptor activates the Akt (protein kinase B)/glycogen synthase kinase-3 signaling pathway via phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase.J Immunol. 1999 Aug 15;163(4):1894-905. J Immunol. 1999. PMID: 10438924
-
The Src family kinase Hck regulates mast cell activation by suppressing an inhibitory Src family kinase Lyn.Blood. 2007 Oct 1;110(7):2511-9. doi: 10.1182/blood-2007-01-066092. Epub 2007 May 18. Blood. 2007. PMID: 17513616 Free PMC article.
-
Immunodeficiencies and haematological disorders--direct connections to cellular signalling pathways.Ann Med. 1997 Dec;29(6):519-29. doi: 10.3109/07853899709007476. Ann Med. 1997. PMID: 9562518 Review.
Cited by
-
Inhibition of c-Fos expression attenuates IgE-mediated mast cell activation and allergic inflammation by counteracting an inhibitory AP1/Egr1/IL-4 axis.J Transl Med. 2021 Jun 15;19(1):261. doi: 10.1186/s12967-021-02932-0. J Transl Med. 2021. PMID: 34130714 Free PMC article.
-
The Critical Role Played by Mitochondrial MITF Serine 73 Phosphorylation in Immunologically Activated Mast Cells.Cells. 2022 Feb 8;11(3):589. doi: 10.3390/cells11030589. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35159398 Free PMC article.
-
SWAP-70 regulates mast cell FcepsilonRI-mediated signaling and anaphylaxis.Eur J Immunol. 2008 Mar;38(3):841-54. doi: 10.1002/eji.200737597. Eur J Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18236401 Free PMC article.
-
NF-kappaB-dependent induction of cathelicidin-related antimicrobial peptide in murine mast cells by lipopolysaccharide.Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2009;150(2):122-32. doi: 10.1159/000218115. Epub 2009 May 11. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19439978 Free PMC article.
-
Prostaglandin E2 activates and utilizes mTORC2 as a central signaling locus for the regulation of mast cell chemotaxis and mediator release.J Biol Chem. 2011 Jan 7;286(1):391-402. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.164772. Epub 2010 Oct 27. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 20980255 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Coffer P.J., Woodgett J.R. Molecular cloning and characterization of a novel putative protein-serine kinase related to the cAMP-dependent and protein kinase C families. Eur. J. Biochem. 1991;201:475–481. - PubMed
-
- Bellacosa A., Testa J.R., Staal S.P., Tsichlis P.N. A retroviral oncogene, akt, encoding a serine-threonine kinase containing an SH2-like region. Science. 1991;254:274–277. - PubMed
-
- Franke T.F., Kaplan D.R., Cantley L.C. PI3Kdownstream AKTion blocks apoptosis. Cell. 1997;88:435–437. - PubMed
-
- Marte B.M., Downward J. PKB/Aktconnecting phosphoinositide 3-kinase to cell survival and beyond. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1997;22:355–358. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

