RSF1, an Arabidopsis locus implicated in phytochrome A signaling
- PMID: 10982420
- PMCID: PMC59120
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.124.1.39
RSF1, an Arabidopsis locus implicated in phytochrome A signaling
Abstract
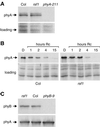
In Arabidopsis, phytochrome A (phyA) is the major photoreceptor both for high irradiance responses to far-red light and broad spectrum very low fluence responses, but little is known of its signaling pathway(s). rsf1 was isolated as a recessive mutant with reduced sensitivity to far-red inhibition of hypocotyl elongation. At the seedling stage rsf1 mutants are affected, to various degrees, in all described phyA-mediated responses. However, in adult rsf1 plants, the photoperiodic flowering response is normal. The rsf1 mutant has wild-type levels of phyA suggesting that RSF1 is required for phyA signaling rather than phyA stability or biosynthesis. RSF1 thus appears to be a major phyA signaling component in seedlings, but not in adult, Arabidopsis plants.
Figures


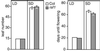
References
-
- Ahmad M, Cashmore AR. The pef mutants of Arabidopsis thaliana define lesions early in the phytochrome signaling pathway. Plant J. 1996;10:1103–1110. - PubMed
-
- Ahmad M, Jarillo JA, Smirnova O, Cashmore AR. The Cry1 blue light photoreceptor of Arabidopsis interacts with phytochrome A in vitro. Mol Cell. 1998;1:939–948. - PubMed
-
- Barnes SA, Quaggio RB, Whitelam GC, Chua N-H. fhy1 defines a branch point in phytochrome A signal transduction pathways for gene expression. Plant J. 1996;10:1155–1161. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

