Induction of postmitotic neuroretina cell proliferation by distinct Ras downstream signaling pathways
- PMID: 10982823
- PMCID: PMC86245
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.20.19.7068-7079.2000
Induction of postmitotic neuroretina cell proliferation by distinct Ras downstream signaling pathways
Abstract
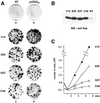
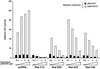
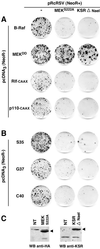
Ras-induced cell transformation is mediated through distinct downstream signaling pathways, including Raf, Ral-GEFs-, and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI 3-kinase)-dependent pathways. In some cell types, strong activation of the Ras-Raf-MEK-extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) cascade leads to cell cycle arrest rather than cell division. We previously reported that constitutive activation of this pathway induces sustained proliferation of primary cultures of postmitotic chicken neuroretina (NR) cells. We used this model system to investigate the respective contributions of Ras downstream signaling pathways in Ras-induced cell proliferation. Three RasV12 mutants (S35, G37, and C40) which differ by their ability to bind to Ras effectors (Raf, Ral-GEFs, and the p110 subunit of PI 3-kinase, respectively) were able to induce sustained NR cell proliferation, although none of these mutants was reported to transform NIH 3T3 cells. Furthermore, they all repressed the promoter of QR1, a neuroretina growth arrest-specific gene. Overexpression of B-Raf or activated versions of Ras effectors Rlf-CAAX and p110-CAAX also induced NR cell division. The mitogenic effect of the RasC40-PI 3-kinase pathway appears to involve Rac and RhoA GTPases but not the antiapoptotic Akt (protein kinase B) signaling. Division induced by RasG37-Rlf appears to be independent of Ral GTPase activation and presumably requires an unidentified mechanism. Activation of either Ras downstream pathway resulted in ERK activation, and coexpression of a dominant negative MEK mutant or mKsr-1 kinase domain strongly inhibited proliferation induced by the three Ras mutants or by their effectors. Similar effects were observed with dominant negative mutants of Rac and Rho. Thus, both the Raf-MEK-ERK and Rac-Rho pathways are absolutely required for Ras-induced NR cell division. Activation of these two pathways by the three distinct Ras downstream effectors possibly relies on an autocrine or paracrine loop, implicating endogenous Ras, since the mitogenic effect of each Ras effector mutant was inhibited by RasN17.
Figures
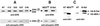



References
-
- Béchade C, Calothy G, Pessac B, Martin P, Coll J, Denhez F, Saule S, Ghysdael J, Stehelin D. Induction of proliferation or transformation of neuroretina cells by the mil and myc viral oncogenes. Nature (London) 1985;316:559–562. - PubMed
-
- Benard V, Bohl B P, Bokoch G M. Characterization of Rac and Cdc42 activation in chemoattractant-stimulated human neutrophils using a novel assay for active GTPases. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:13198–13204. - PubMed
-
- Brunet A, Pages G, Pouyssegur J. Constitutively active mutants of MAP kinase kinase (MEK1) induce growth factor-relaxation and oncogenicity when expressed in fibroblasts. Oncogene. 1994;9:3379–3387. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
