H-NS mediated compaction of DNA visualised by atomic force microscopy
- PMID: 10982869
- PMCID: PMC110753
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/28.18.3504
H-NS mediated compaction of DNA visualised by atomic force microscopy
Abstract
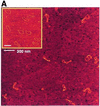
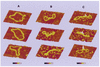
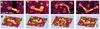
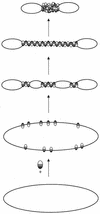
The Escherichia coli H-NS protein is a nucleoid-associated protein involved in gene regulation and DNA compaction. To get more insight into the mechanism of DNA compaction we applied atomic force microscopy (AFM) to study the structure of H-NS-DNA complexes. On circular DNA molecules two different levels of H-NS induced condensation were observed. H-NS induced lateral condensation of large regions of the plasmid. In addition, large globular structures were identified that incorporated a considerable amount of DNA. The formation of these globular structures appeared not to be dependent on any specific sequence. On the basis of the AFM images, a model for global condensation of the chromosomal DNA by H-NS is proposed.
Figures




References
-
- Jacquet M., Cukier-Kahn,R., Pla,J. and Gros,F. (1971) Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 45, 1597–1607. - PubMed
-
- Goosen N. and van de Putte,P. (1995) Mol. Microbiol., 16, 1–7. - PubMed
-
- Finkel S.E. and Johnson,R.C. (1992) Mol. Microbiol., 6, 3257–3265. - PubMed
-
- Lucht J.M., Dersch,P., Kempf,B. and Bremer,E. (1994) J. Biol. Chem., 269, 6578. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

