Two novel human and mouse DNA polymerases of the polX family
- PMID: 10982892
- PMCID: PMC110747
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/28.18.3684
Two novel human and mouse DNA polymerases of the polX family
Abstract
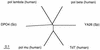
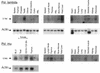
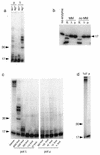
We describe here two novel mouse and human DNA polymerases: one (pol lambda) has homology with DNA polymerase beta while the other one (pol mu) is closer to terminal deoxynucleotidyltransferase. However both have DNA polymerase activity in vitro and share similar structural organization, including a BRCT domain, helix-loop-helix DNA-binding motifs and polymerase X domain. mRNA expression of pol lambda is highest in testis and fetal liver, while expression of pol mu is more lymphoid, with highest expression both in thymus and tonsillar B cells. An unusually large number of splice variants is observed for the pol mu gene, most of which affect the polymerase domain. Expression of mRNA of both polymerases is down-regulated upon treatment by DNA damaging agents (UV light, gamma-rays or H(2)O(2)). This suggests that their biological function may differ from DNA translesion synthesis, for which several DNA polymerase activities have been recently described. Possible functions are discussed.
Figures

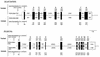



Similar articles
-
DNA polymerase lambda (Pol lambda), a novel eukaryotic DNA polymerase with a potential role in meiosis.J Mol Biol. 2000 Aug 25;301(4):851-67. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.2000.4005. J Mol Biol. 2000. PMID: 10966791
-
Homology modeling of four Y-family, lesion-bypass DNA polymerases: the case that E. coli Pol IV and human Pol kappa are orthologs, and E. coli Pol V and human Pol eta are orthologs.J Mol Graph Model. 2006 Sep;25(1):87-102. doi: 10.1016/j.jmgm.2005.10.009. Epub 2006 Jan 4. J Mol Graph Model. 2006. PMID: 16386932
-
A comparison of BRCT domains involved in nonhomologous end-joining: introducing the solution structure of the BRCT domain of polymerase lambda.DNA Repair (Amst). 2008 Aug 2;7(8):1340-51. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2008.04.018. Epub 2008 Jun 26. DNA Repair (Amst). 2008. PMID: 18585102 Free PMC article.
-
Escherichia coli Y family DNA polymerases.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2011 Jun 1;16(8):3164-82. doi: 10.2741/3904. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2011. PMID: 21622227 Review.
-
Properties and functions of Escherichia coli: Pol IV and Pol V.Adv Protein Chem. 2004;69:229-64. doi: 10.1016/S0065-3233(04)69008-5. Adv Protein Chem. 2004. PMID: 15588845 Review.
Cited by
-
Structural evidence for an in trans base selection mechanism involving Loop1 in polymerase μ at an NHEJ double-strand break junction.J Biol Chem. 2019 Jul 5;294(27):10579-10595. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.008739. Epub 2019 May 28. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 31138645 Free PMC article.
-
Translesion DNA synthesis in the context of cancer research.Cancer Cell Int. 2011 Nov 2;11:39. doi: 10.1186/1475-2867-11-39. Cancer Cell Int. 2011. PMID: 22047021 Free PMC article.
-
AP endonuclease knockdown enhances methyl methanesulfonate hypersensitivity of DNA polymerase β knockout mouse embryonic fibroblasts.J Radiat Res. 2015 May;56(3):462-6. doi: 10.1093/jrr/rru125. Epub 2015 Feb 26. J Radiat Res. 2015. PMID: 25724755 Free PMC article.
-
Resolution of complex ends by Nonhomologous end joining - better to be lucky than good?Genome Integr. 2012 Dec 31;3(1):10. doi: 10.1186/2041-9414-3-10. Genome Integr. 2012. PMID: 23276302 Free PMC article.
-
Association of DNA polymerase mu (pol mu) with Ku and ligase IV: role for pol mu in end-joining double-strand break repair.Mol Cell Biol. 2002 Jul;22(14):5194-202. doi: 10.1128/MCB.22.14.5194-5202.2002. Mol Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 12077346 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Diaz M., Velez,J., Singh,M., Cerny,J. and Flajnik,M.F. (1999) Int. Immunol., 11, 825–833. - PubMed
-
- Masutani C., Kusumoto,R., Yamada,A., Dohmae,N., Yokoi,M., Yuasa,M., Araki,M., Iwai,S., Takio,K. and Hanaoka,F. (1999) Nature, 399, 700–704. - PubMed
-
- McDonald J.P., Rapic-Otrin,V., Epstein,J.A., Broughton,B.C., Wang,X., Lehmann,A.R., Wolgemuth,D.J. and Woodgate,R. (1999) Genomics, 60, 20–30. - PubMed
-
- Ogi T., Kato,T.,Jr, Kato,T. and Ohmori,H. (1999) Genes Cells, 4, 607–618. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

