Contribution of Salmonella typhimurium type III secretion components to needle complex formation
- PMID: 10984518
- PMCID: PMC27139
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.200209497
Contribution of Salmonella typhimurium type III secretion components to needle complex formation
Abstract
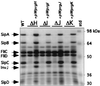
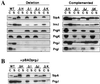
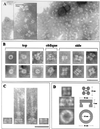
The prgHIJK operon encodes components of the Salmonella typhimurium pathogenicity island 1 type III secretion system (TTSS). Previously, prgH and prgK were shown to be required for formation of the supramolecular type III secretion needle complex (NC) [Kubori, T., et al. (1998) Science 280, 602-605]. This work indicates that all prg operon genes are required for NC formation. PrgH multimerizes into a distinct tetrameric-shaped structure that may be an early intermediate of NC assembly and may provide the structural foundation required for PrgK oligomerization. PrgH and PrgK, in the absence of other TTSS components, oligomerize into ring-shaped structures identical in appearance and size to the base of the NC, indicating that they are likely the major inner membrane structural components required for secretion. PrgI and PrgJ cofractionate with the NC and are secreted into the culture supernatant. NC from prgI and prgJ mutants have an identical morphology to the envelope-spanning (basal body) NC components, but are missing the external needle, indicating that PrgI and PrgJ are required for full NC assembly and are likely components of the external needle. Therefore, PrgI and PrgJ are secreted through the NC basal body, composed in part of PrgH/K and InvG/H rings, to participate in assembly of the more distal components of the NC.
Figures


References
-
- Mandell G L, Douglas R G, Bennett J E. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett's Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. 4th Ed. New York: Churchill Livingstone; 1995. p. 2.
-
- Hensel M, Shea J E, Gleeson C, Jones M D, Dalton E, Holden D W. Science. 1995;269:400–403. - PubMed
-
- Kubori T, Matsushima Y, Nakamura D, Uralil J, Lara-Tejero M, Sukhan A, Galan J E, Aizawa S I. Science. 1998;280:602–605. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

