Automated de novo sequencing of proteins by tandem high-resolution mass spectrometry
- PMID: 10984529
- PMCID: PMC27020
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.97.19.10313
Automated de novo sequencing of proteins by tandem high-resolution mass spectrometry
Abstract
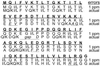
A de novo sequencing program for proteins is described that uses tandem MS data from electron capture dissociation and collisionally activated dissociation of electrosprayed protein ions. Computer automation is used to convert the fragment ion mass values derived from these spectra into the most probable protein sequence, without distinguishing Leu/Ile. Minimum human input is necessary for the data reduction and interpretation. No extra chemistry is necessary to distinguish N- and C-terminal fragments in the mass spectra, as this is determined from the electron capture dissociation data. With parts-per-million mass accuracy (now available by using higher field Fourier transform MS instruments), the complete sequences of ubiquitin (8.6 kDa) and melittin (2.8 kDa) were predicted correctly by the program. The data available also provided 91% of the cytochrome c (12.4 kDa) sequence (essentially complete except for the tandem MS-resistant region K(13)-V(20) that contains the cyclic heme). Uncorrected mass values from a 6-T instrument still gave 86% of the sequence for ubiquitin, except for distinguishing Gln/Lys. Extensive sequencing of larger proteins should be possible by applying the algorithm to pieces of approximately 10-kDa size, such as products of limited proteolysis.
Figures




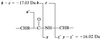
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

