Complex promoter and coding region beta 2-adrenergic receptor haplotypes alter receptor expression and predict in vivo responsiveness
- PMID: 10984540
- PMCID: PMC27050
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.97.19.10483
Complex promoter and coding region beta 2-adrenergic receptor haplotypes alter receptor expression and predict in vivo responsiveness
Abstract
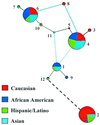
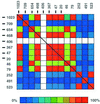
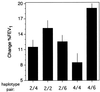
The human beta(2)-adrenergic receptor gene has multiple single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), but the relevance of chromosomally phased SNPs (haplotypes) is not known. The phylogeny and the in vitro and in vivo consequences of variations in the 5' upstream and ORF were delineated in a multiethnic reference population and an asthmatic cohort. Thirteen SNPs were found organized into 12 haplotypes out of the theoretically possible 8,192 combinations. Deep divergence in the distribution of some haplotypes was noted in Caucasian, African-American, Asian, and Hispanic-Latino ethnic groups with >20-fold differences among the frequencies of the four major haplotypes. The relevance of the five most common beta(2)-adrenergic receptor haplotype pairs was determined in vivo by assessing the bronchodilator response to beta agonist in asthmatics. Mean responses by haplotype pair varied by >2-fold, and response was significantly related to the haplotype pair (P = 0.007) but not to individual SNPs. Expression vectors representing two of the haplotypes differing at eight of the SNP loci and associated with divergent in vivo responsiveness to agonist were used to transfect HEK293 cells. beta(2)-adrenergic receptor mRNA levels and receptor density in cells transfected with the haplotype associated with the greater physiologic response were approximately 50% greater than those transfected with the lower response haplotype. The results indicate that the unique interactions of multiple SNPs within a haplotype ultimately can affect biologic and therapeutic phenotype and that individual SNPs may have poor predictive power as pharmacogenetic loci.
Figures
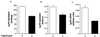
References
-
- Reihsaus E, Innis M, MacIntyre N, Liggett S B. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1993;8:334–339. - PubMed
-
- Green S A, Cole G, Jacinto M, Innis M, Liggett S B. J Biol Chem. 1993;268:23116–23121. - PubMed
-
- Green S, Turki J, Innis M, Liggett S B. Biochemistry. 1994;33:9414–9419. - PubMed
-
- Green S A, Turki J, Bejarano P, Hall I P, Liggett S B. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1995;13:25–33. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

