Erythropoietin crosses the blood-brain barrier to protect against experimental brain injury
- PMID: 10984541
- PMCID: PMC27058
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.97.19.10526
Erythropoietin crosses the blood-brain barrier to protect against experimental brain injury
Abstract
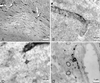
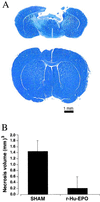
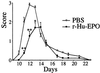
Erythropoietin (EPO), recognized for its central role in erythropoiesis, also mediates neuroprotection when the recombinant form (r-Hu-EPO) is directly injected into ischemic rodent brain. We observed abundant expression of the EPO receptor at brain capillaries, which could provide a route for circulating EPO to enter the brain. In confirmation of this hypothesis, systemic administration of r-Hu-EPO before or up to 6 h after focal brain ischemia reduced injury by approximately 50-75%. R-Hu-EPO also ameliorates the extent of concussive brain injury, the immune damage in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis, and the toxicity of kainate. Given r-Hu-EPO's excellent safety profile, clinical trials evaluating systemically administered r-Hu-EPO as a general neuroprotective treatment are warranted.
Figures


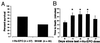
References
-
- Juul S E, Stallings S A, Christensen R D. Pediatr Res. 1999;46:543–547. - PubMed
-
- Juul S E, Anderson D K, Li Y, Christensen R D. Pediatr Res. 1998;43:40–49. - PubMed
-
- Marti H H, Wenger R H, Rivas L A, Straumann U, Digicaylioglu M, Henn V, Yonekawa Y, Bauer C, Gassmann M. Eur J Neurosci. 1996;8:666–676. - PubMed
-
- Masuda S, Okano M, Yamagishi K, Nagao M, Ueda M, Sasaki R. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:19488–19493. - PubMed
-
- Sadamoto Y, Igase K, Sakanaka M, Sato K, Otsuka H, Sakaki S, Masuda S, Sasaki R. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1998;253:26–32. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

