RIC-8 (Synembryn): a novel conserved protein that is required for G(q)alpha signaling in the C. elegans nervous system
- PMID: 10985349
- PMCID: PMC4704990
- DOI: 10.1016/s0896-6273(00)00037-4
RIC-8 (Synembryn): a novel conserved protein that is required for G(q)alpha signaling in the C. elegans nervous system
Abstract
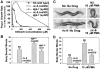
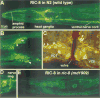
Recent studies describe a network of signaling proteins centered around G(o)alpha and G(q)alpha that regulates neurotransmitter secretion in C. elegans by controlling the production and consumption of diacylglycerol (DAG). We sought other components of the Goalpha-G(q)alpha signaling network by screening for aldicarb-resistant mutants with phenotypes similar to egl-30 (G(q)alpha) mutants. In so doing, we identified ric-8, which encodes a novel protein named RIC-8 (synembryn). Through cDNA analysis, we show that RIC-8 is conserved in vertebrates. Through immunostaining, we show that RIC-8 is concentrated in the cytoplasm of neurons. Exogenous application of phorbol esters or loss of DGK-1 (diacylglycerol kinase) rescues ric-8 mutant phenotypes. A genetic analysis suggests that RIC-8 functions upstream of, or in conjunction with, EGL-30 (G(q)alpha).
Figures





References
-
- Berman DM, Wilkie TM, Gilman AG. GAIP and RGS4 are GTPase-activating proteins for the Gi subfamily of G protein α subunits. Cell. 1996;86:445–452. - PubMed
-
- Cambon C, Declume C, Derache R. Effect of the insecticidal carbamate derivatives (carbofuran, pirimicarb, aldicarb) on the activity of acetylcholinesterase in tissues from pregnant rats and fetuses. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1979;49:203–208. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

