oriT-directed cloning of defined large regions from bacterial genomes: identification of the Sinorhizobium meliloti pExo megaplasmid replicator region
- PMID: 10986253
- PMCID: PMC110993
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.182.19.5486-5494.2000
oriT-directed cloning of defined large regions from bacterial genomes: identification of the Sinorhizobium meliloti pExo megaplasmid replicator region
Abstract
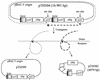
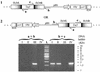
We have developed a procedure to directly clone large fragments from the genome of the soil bacterium Sinorhizobium meliloti. Specific regions to be cloned are first flanked by parallel copies of an origin of transfer (oriT) together with a plasmid replication origin capable of replicating large clones in Escherichia coli but not in the target organism. Supplying transfer genes in trans specifically transfers the oriT-flanked region, and in this process, site-specific recombination at the oriT sites results in a plasmid carrying the flanked region of interest that can replicate in E. coli from the inserted origin of replication (in this case, the F origin carried on a BAC cloning vector). We have used this procedure with the oriT of the plasmid RK2 to clone contiguous fragments of 50, 60, 115, 140, 240, and 200 kb from the S. meliloti pExo megaplasmid. Analysis of the 60-kb fragment allowed us to identify a 9-kb region capable of autonomous replication in the bacterium Agrobacterium tumefaciens. The nucleotide sequence of this fragment revealed a replicator region including homologs of the repA, repB, and repC genes from other Rhizobiaceae, which encode proteins involved in replication and segregation of plasmids in many organisms.
Figures
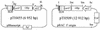




Similar articles
-
A Family of Single Copy repABC-Type Shuttle Vectors Stably Maintained in the Alpha-Proteobacterium Sinorhizobium meliloti.ACS Synth Biol. 2017 Jun 16;6(6):968-984. doi: 10.1021/acssynbio.6b00320. Epub 2017 Mar 20. ACS Synth Biol. 2017. PMID: 28264559 Free PMC article.
-
Isolation and characterization of a DNA replication origin from the 1,700-kilobase-pair symbiotic megaplasmid pSym-b of Rhizobium meliloti.J Bacteriol. 1993 Oct;175(20):6553-61. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.20.6553-6561.1993. J Bacteriol. 1993. PMID: 8407832 Free PMC article.
-
Replication regions of Sinorhizobium meliloti plasmids.Plasmid. 2006 Mar;55(2):87-98. doi: 10.1016/j.plasmid.2005.08.003. Epub 2005 Oct 3. Plasmid. 2006. PMID: 16202450
-
Genetic and functional characterization of a yet-unclassified rhizobial Dtr (DNA-transfer-and-replication) region from a ubiquitous plasmid conjugal system present in Sinorhizobium meliloti, in Sinorhizobium medicae, and in other nonrhizobial Gram-negative bacteria.Plasmid. 2012 May;67(3):199-210. doi: 10.1016/j.plasmid.2011.12.010. Epub 2012 Jan 2. Plasmid. 2012. PMID: 22233546
-
The Plasmid Mobilome of the Model Plant-Symbiont Sinorhizobium meliloti: Coming up with New Questions and Answers.Microbiol Spectr. 2014 Oct;2(5). doi: 10.1128/microbiolspec.PLAS-0005-2013. Microbiol Spectr. 2014. PMID: 26104371 Review.
Cited by
-
A Family of Single Copy repABC-Type Shuttle Vectors Stably Maintained in the Alpha-Proteobacterium Sinorhizobium meliloti.ACS Synth Biol. 2017 Jun 16;6(6):968-984. doi: 10.1021/acssynbio.6b00320. Epub 2017 Mar 20. ACS Synth Biol. 2017. PMID: 28264559 Free PMC article.
-
An improved method for oriT-directed cloning and functionalization of large bacterial genomic regions.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2013 Aug;79(16):4869-78. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00994-13. Epub 2013 Jun 7. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23747708 Free PMC article.
-
The complete sequence of the 1,683-kb pSymB megaplasmid from the N2-fixing endosymbiont Sinorhizobium meliloti.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001 Aug 14;98(17):9889-94. doi: 10.1073/pnas.161294698. Epub 2001 Jul 31. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001. PMID: 11481431 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of the partitioning site within the repABC-type replicon of the composite Paracoccus versutus plasmid pTAV1.J Bacteriol. 2001 Nov;183(21):6234-43. doi: 10.1128/JB.183.21.6234-6243.2001. J Bacteriol. 2001. PMID: 11591666 Free PMC article.
-
Genome engineering and direct cloning of antibiotic gene clusters via phage ϕBT1 integrase-mediated site-specific recombination in Streptomyces.Sci Rep. 2015 Mar 4;5:8740. doi: 10.1038/srep08740. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 25737113 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Banfalvi Z, Kondorosi E, Kondorosi A. Rhizobium meliloti carries two megaplasmids. Plasmid. 1985;13:129–138. - PubMed
-
- Banfalvi Z, Sakanyan V, Koncz C, Kiss A, Dusha I, Kondorosi A. Location of nodulation and nitrogen fixation genes on a high molecular weight plasmid of R. meliloti. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;184:318–325. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

