Pathogenic neisseriae can use hemoglobin, transferrin, and lactoferrin independently of the tonB locus
- PMID: 10986265
- PMCID: PMC111005
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.182.19.5586-5591.2000
Pathogenic neisseriae can use hemoglobin, transferrin, and lactoferrin independently of the tonB locus
Abstract
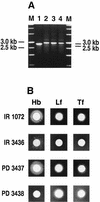
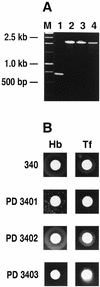
Redundant TonB systems which function in iron transport from TonB-dependent ligands have recently been identified in several gram-negative bacteria. We demonstrate here that in addition to the previously described tonB locus, an alternative system exists for the utilization of iron from hemoglobin, transferrin, or lactoferrin in Neisseria meningitidis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Following incubation on media containing hemoglobin, N. meningitidis IR3436 (tonB exbB exbD deletion mutant) and N. gonorrhoeae PD3401 (tonB insertional mutant) give rise to colonies which can grow with hemoglobin. Transfer of Hb(+) variants (PD3437 or PD3402) to media containing hemoglobin, transferrin, and/or lactoferrin as sole iron sources resulted in growth comparable to that observed for the wild-type strains. Transformation of N. meningitidis IR3436 or N. gonorrhoeae PD3401 with chromosomal DNA from the Hb(+) variants yielded transformants capable of growth with hemoglobin. When we inactivated the TonB-dependent outer membrane hemoglobin receptors (HmbR or HpuB) in the Neisseria Hb(+) variants, these strains could not grow with hemoglobin; however, growth was observed with transferrin and/or lactoferrin. These results demonstrate that accumulation of iron from hemoglobin, transferrin, and lactoferrin in the pathogenic neisseriae can occur via a system that is independent of the previously described tonB locus.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Neisseria meningitidis tonB, exbB, and exbD genes: Ton-dependent utilization of protein-bound iron in Neisseriae.J Bacteriol. 1997 Feb;179(3):805-12. doi: 10.1128/jb.179.3.805-812.1997. J Bacteriol. 1997. PMID: 9006036 Free PMC article.
-
Cloning and functional characterization of Neisseria gonorrhoeae tonB, exbB and exbD genes.Mol Microbiol. 1997 Apr;24(1):169-79. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.1997.3421692.x. Mol Microbiol. 1997. PMID: 9140974
-
HmbR outer membrane receptors of pathogenic Neisseria spp.: iron-regulated, hemoglobin-binding proteins with a high level of primary structure conservation.J Bacteriol. 1996 Aug;178(15):4670-8. doi: 10.1128/jb.178.15.4670-4678.1996. J Bacteriol. 1996. PMID: 8755899 Free PMC article.
-
Response of Neisseria meningitidis to iron limitation.Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1997 Feb;71(1-2):129-36. doi: 10.1023/a:1000179301748. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1997. PMID: 9049024 Review.
-
Iron transport systems in Neisseria meningitidis.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2004 Mar;68(1):154-71. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.68.1.154-171.2004. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2004. PMID: 15007100 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Characterization of binding of human lactoferrin to pneumococcal surface protein A.Infect Immun. 2001 May;69(5):3372-81. doi: 10.1128/IAI.69.5.3372-3381.2001. Infect Immun. 2001. PMID: 11292760 Free PMC article.
-
Growth of Neisseria gonorrhoeae in the female mouse genital tract does not require the gonococcal transferrin or hemoglobin receptors and may be enhanced by commensal lactobacilli.Infect Immun. 2002 May;70(5):2549-58. doi: 10.1128/IAI.70.5.2549-2558.2002. Infect Immun. 2002. PMID: 11953395 Free PMC article.
-
Interactions between the outer membrane ferric citrate transporter FecA and TonB: studies of the FecA TonB box.J Bacteriol. 2003 Mar;185(6):1870-85. doi: 10.1128/JB.185.6.1870-1885.2003. J Bacteriol. 2003. PMID: 12618451 Free PMC article.
-
PspA protects Streptococcus pneumoniae from killing by apolactoferrin, and antibody to PspA enhances killing of pneumococci by apolactoferrin [corrected].Infect Immun. 2004 Sep;72(9):5031-40. doi: 10.1128/IAI.72.9.5031-5040.2004. Infect Immun. 2004. PMID: 15321996 Free PMC article.
-
Iron Acquisition Systems of Gram-negative Bacterial Pathogens Define TonB-Dependent Pathways to Novel Antibiotics.Chem Rev. 2021 May 12;121(9):5193-5239. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.0c01005. Epub 2021 Mar 16. Chem Rev. 2021. PMID: 33724814 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Biswas G D, Anderson J E, Sparling P F. Cloning and characterization of Neisseria gonorrhoeae tonB, exbB and exbD genes. Mol Microbiol. 1997;24:169–179. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

