FSY1, a novel gene encoding a specific fructose/H(+) symporter in the type strain of Saccharomyces carlsbergensis
- PMID: 10986274
- PMCID: PMC111014
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.182.19.5628-5630.2000
FSY1, a novel gene encoding a specific fructose/H(+) symporter in the type strain of Saccharomyces carlsbergensis
Abstract
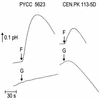
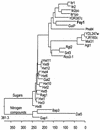
A novel gene, FSY1, encoding a permease involved in active fructose uptake by a proton symport mechanism in the type strain of Saccharomyces carlsbergensis has been isolated. Fsy1p is only distantly related to the Hxt proteins that mediate facilitated diffusion of glucose and fructose in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and related species.
Figures

References
-
- Cason D T, Spencer-Martins I, van Uden N. Transport of fructose by a proton symport in a brewing yeast. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1986;36:307–309.
-
- Diderich J A, Schepper M, van Hoek P, Luttik M A, van Dijken J P, Pronk J T, Klaassen P, Boelens H F, de Mattos M J, van Dam K, Kruckeberg A L. Glucose uptake kinetics and transcription of HXT genes in chemostat cultures of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:15350–15359. - PubMed
-
- Gietz R D, Sugino A. New yeast-Escherichia coli shuttle vectors constructed with in vitro mutagenized yeast genes lacking six-base pair restriction sites. Gene. 1988;74:527–534. - PubMed
-
- Gietz R D, Schiestl R H, Willems A R, Woods R A. Studies on the transformation of intact yeast cells by the LiAc/ss-DNA/PEG procedure. Yeast. 1995;11:355–360. - PubMed
-
- Kasahara M, Maeda M. Contribution to substrate recognition of two aromatic amino acid residues in putative transmembrane segment 10 of the yeast sugar transporters Gal2 and Hxt2. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:29106–29112. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

