p53 transcriptional activity is essential for p53-dependent apoptosis following DNA damage
- PMID: 10990460
- PMCID: PMC314218
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/19.18.4967
p53 transcriptional activity is essential for p53-dependent apoptosis following DNA damage
Abstract
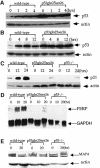
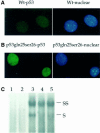
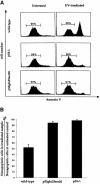
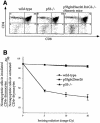
p53-mediated transcription activity is essential for cell cycle arrest, but its importance for apoptosis remains controversial. To address this question, we employed homologous recombination and LoxP/Cre-mediated deletion to produce mutant murine embryonic stem (ES) cells that express p53 with Gln and Ser in place of Leu25 and Trp26, respectively. p53(Gln25Ser26) was stable but did not accumulate after DNA damage; the expression of p21/Waf1 and PERP was not induced, and p53-dependent repression of MAP4 expression was abolished. Therefore, p53(Gln25Ser26) is completely deficient in transcriptional activation and repression activities. After DNA damage by UV radiation, p53(Gln25Ser26) was phosphorylated at Ser18 but was not acetylated at C-terminal sites, and its DNA binding activity did not increase, further supporting a role for p53 acetylation in the activation of sequence-specific DNA binding activity. Most importantly, p53(Gln25Ser26) mouse thymocytes and ES cells, like p53(-/-) cells, did not undergo DNA damage-induced apoptosis. We conclude that the transcriptional activities of p53 are required for p53-dependent apoptosis.
Figures


References
-
- Aladjem M.I., Spike,B.T., Rodewald,L.W., Hope,T.J., Klemm,M., Jaenisch,R. and Wahl,G.M. (1998) ES cells do not activate p53-dependent stress responses and undergo p53-independent apoptosis in response to DNA damage. Curr. Biol., 8, 145–155. - PubMed
-
- Banin S. et al. (1998) Enhanced phosphorylation of p53 by ATM in response to DNA damage. Science, 281, 1674–1677. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

