Deficiency of T2K leads to apoptotic liver degeneration and impaired NF-kappaB-dependent gene transcription
- PMID: 10990461
- PMCID: PMC314216
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/19.18.4976
Deficiency of T2K leads to apoptotic liver degeneration and impaired NF-kappaB-dependent gene transcription
Abstract
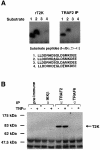
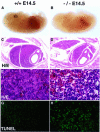
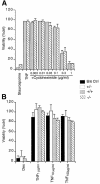
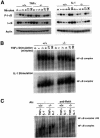
Induction of NF-kappaB-dependent transcription requires phosphorylation and subsequent degradation of I-kappaB, an inhibitor of NF-kappaB, followed by nuclear translocation and DNA binding of NF-kappaB. Tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 2 (TRAF2) plays a role in NF-kappaB activation in response to cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNFalpha). In this study, we purified and characterized a novel kinase (T2K, also known as TBK1 or NAK), which associates with TRAF2 and exhibits kinase activity towards I-kappaBalpha in vitro. The physiological function of T2K was investigated using T2K-deficient mice. Heterozygotes appear normal, but t2k(-/-) animals die at approximately E14.5 of massive liver degeneration and apoptosis. Never theless, hematopoietic progenitors from T2K-deficient fetal liver support normal lymphocyte development. Furthermore, t2k(-/-) embryonic fibroblasts and thymocytes do not display increased sensitivity to TNFalpha-induced apoptosis. In response to either TNFalpha or IL-1 induction, t2k(-/-) embryonic fibroblasts exhibit normal degradation of I-kappaB and kappaB-binding activity. However, NF-kappaB-directed transcription is dramatically reduced. These results demonstrate that, like I-kappaB kinase beta and the RelA subunit of NF-kappaB, T2K is critical in protecting embryonic liver from apoptosis. However, T2K has a unique role in the activation of NF-kappaB-directed transcription, apparently independent of I-kappaB degradation and NF-kappaB DNA binding.
Figures

References
-
- Amakawa R. et al. (1996) Impaired negative selection of T cells in Hodgkin’s disease antigen CD30-deficient mice. Cell, 84, 551–562. - PubMed
-
- Anrather J., Csizmadia,V., Soares,M.P. and Winkler,H. (1999) Regulation of NF-κB RelA phosphorylation and transcriptional activity by p21(ras) and protein kinase Cζ in primary endothelial cells. J. Biol. Chem., 274, 13594–13603. - PubMed
-
- Arch R.H., Gedrich,R.W. and Thompson,C.B. (1998) Tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factors (TRAFs)—a family of adapter proteins that regulates life and death. Genes Dev., 12, 2821–2830. - PubMed
-
- Beg A.A. and Baltimore,D. (1996) An essential role for NF-κB in preventing TNF-α-induced cell death. Science, 274, 782–784. - PubMed
-
- Beg A.A., Sha,W.C., Bronson,R.T., Ghosh,S. and Baltimore,D. (1995) Embryonic lethality and liver degeneration in mice lacking the RelA component of NF-kB. Nature, 376, 167–170. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

