Recombinant bovine interleukin-1beta amplifies the effects of partially purified Pasteurella haemolytica leukotoxin on bovine neutrophils in a beta(2)-integrin-dependent manner
- PMID: 10992457
- PMCID: PMC101509
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.68.10.5581-5586.2000
Recombinant bovine interleukin-1beta amplifies the effects of partially purified Pasteurella haemolytica leukotoxin on bovine neutrophils in a beta(2)-integrin-dependent manner
Abstract
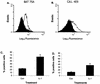
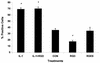
The influx and death of polymorphonuclear leukocytes within the infected lung are hallmarks of bovine pasteurellosis. Recent reports have shown that the Pasteurella haemolytica leukotoxin (LKT) and other RTX toxins bind beta(2)-integrins on target cells. In this study we demonstrate that exposure of bovine neutrophils to recombinant bovine interleukin-1beta upregulates beta(2)-integrins (CD11a/CD18), which in turn enhance the binding and amplify the biological effects of partially purified LKT on these cells. LKT binding and cytotoxicity were inhibited by addition of an anti-integrin antibody (CD11a/CD18). These findings help to clarify the early events that occur in bovine pasteurellosis and support the hypothesis that inflammatory mediators might increase the severity of pasteurellosis by causing upregulation of beta(2)-integrins that serve as an LKT receptor on bovine neutrophils.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Inflammatory cytokines enhance the interaction of Mannheimia haemolytica leukotoxin with bovine peripheral blood neutrophils in vitro.Infect Immun. 2002 Aug;70(8):4336-43. doi: 10.1128/IAI.70.8.4336-4343.2002. Infect Immun. 2002. PMID: 12117943 Free PMC article.
-
Prior exposure to Mannheimia haemolytica leukotoxin or LPS enhances beta(2)-integrin expression by bovine neutrophils and augments LKT cytotoxicity.Microb Pathog. 2003 Jun;34(6):267-75. doi: 10.1016/s0882-4010(03)00060-3. Microb Pathog. 2003. PMID: 12782479
-
Lymphocyte function-associated antigen 1 is a receptor for Pasteurella haemolytica leukotoxin in bovine leukocytes.Infect Immun. 2000 Jan;68(1):72-9. doi: 10.1128/IAI.68.1.72-79.2000. Infect Immun. 2000. PMID: 10603370 Free PMC article.
-
[Mannheimia haemolytica and the pathogenesis of enzootic bronchopneumonia].Berl Munch Tierarztl Wochenschr. 2004 Mar-Apr;117(3-4):97-115. Berl Munch Tierarztl Wochenschr. 2004. PMID: 15046457 Review. German.
-
Role of Mannheimia haemolytica leukotoxin in the pathogenesis of bovine pneumonic pasteurellosis.Anim Health Res Rev. 2002 Dec;3(2):69-82. doi: 10.1079/ahrr200242. Anim Health Res Rev. 2002. PMID: 12665107 Review.
Cited by
-
Inflammatory cytokines enhance the interaction of Mannheimia haemolytica leukotoxin with bovine peripheral blood neutrophils in vitro.Infect Immun. 2002 Aug;70(8):4336-43. doi: 10.1128/IAI.70.8.4336-4343.2002. Infect Immun. 2002. PMID: 12117943 Free PMC article.
-
RTX Toxins Ambush Immunity's First Cellular Responders.Toxins (Basel). 2019 Dec 10;11(12):720. doi: 10.3390/toxins11120720. Toxins (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31835552 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of experimental infection of cattle with bovine herpesvirus-1 (BHV-1) on the ex vivo interaction of bovine leukocytes with Mannheimia (Pasteurella) haemolytica leukotoxin.Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2002 Jan 1;84(1-2):97-110. doi: 10.1016/s0165-2427(01)00397-x. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2002. PMID: 11825601 Free PMC article.
-
Mannheimia haemolytica leukotoxin activates a nonreceptor tyrosine kinase signaling cascade in bovine leukocytes, which induces biological effects.Infect Immun. 2001 Oct;69(10):6131-9. doi: 10.1128/IAI.69.10.6131-6139.2001. Infect Immun. 2001. PMID: 11553552 Free PMC article.
-
RTX proteins: a highly diverse family secreted by a common mechanism.FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2010 Nov;34(6):1076-112. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6976.2010.00231.x. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2010. PMID: 20528947 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ambagala T C, Ambagala A P N, Srikumaran S. The leukotoxin of Pasteurella haemolytica binds to integrins on bovine leukocytes. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1999;179:161–167. - PubMed
-
- Baluyut C S, Simonson R R, Bemrick W J, Maheswaran S K. Interaction of Pasteurella haemolytica with bovine neutrophils: identification and partial characterization of a cytotoxin. Am J Vet Res. 1981;42:1920–1926. - PubMed
-
- Breider M A, Yang Z. Tissue factor expression in bovine endothelial cells induced by Pasteurella haemolytica lipopolysaccharide and interleukin-1. Vet Pathol. 1994;31:55–60. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

