Absence of alpha-syntrophin leads to structurally aberrant neuromuscular synapses deficient in utrophin
- PMID: 10995443
- PMCID: PMC2150701
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.150.6.1385
Absence of alpha-syntrophin leads to structurally aberrant neuromuscular synapses deficient in utrophin
Abstract
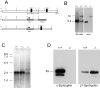
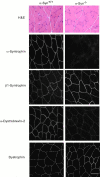
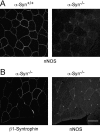
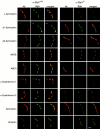
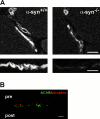
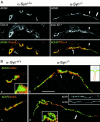
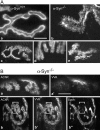
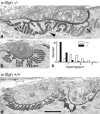
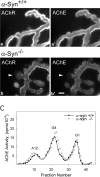
The syntrophins are a family of structurally related proteins that contain multiple protein interaction motifs. Syntrophins associate directly with dystrophin, the product of the Duchenne muscular dystrophy locus, and its homologues. We have generated alpha-syntrophin null mice by targeted gene disruption to test the function of this association. The alpha-Syn(-/)- mice show no evidence of myopathy, despite reduced levels of alpha-dystrobrevin-2. Neuronal nitric oxide synthase, a component of the dystrophin protein complex, is absent from the sarcolemma of the alpha-Syn(-/)- mice, even where other syntrophin isoforms are present. alpha-Syn(-/)- neuromuscular junctions have undetectable levels of postsynaptic utrophin and reduced levels of acetylcholine receptor and acetylcholinesterase. The mutant junctions have shallow nerve gutters, abnormal distributions of acetylcholine receptors, and postjunctional folds that are generally less organized and have fewer openings to the synaptic cleft than controls. Thus, alpha-syntrophin has an important role in synapse formation and in the organization of utrophin, acetylcholine receptor, and acetylcholinesterase at the neuromuscular synapse.
Figures
References
-
- Adams M.E., Butler M.H., Dwyer T.M., Peters M.F., Murnane A.A., Froehner S.C. Two forms of mouse syntrophin, a 58 kd dystrophin-associated protein, differ in primary structure and tissue distribution. Neuron. 1993;11:531–540. - PubMed
-
- Adams M.E., Dwyer T.M., Dowler L.L., White R.A., Froehner S.C. Mouse alpha 1- and beta 2-syntrophin gene structure, chromosome localization, and homology with a discs large domain. J. Biol. Chem. 1995;270:25859–25865. - PubMed
-
- Ahn A.H., Freener C.A., Gussoni E., Yoshida M., Ozawa E., Kunkel L.M. The three human syntrophin genes are expressed in diverse tissues, have distinct chromosomal locations, and each bind to dystrophin and its relatives. J. Biol. Chem. 1996;271:2724–2730. - PubMed
-
- Bewick G.S., Nicholson L.V.B., Young C., O'Donnell E., Slater C.R. Different distributions of dystrophin and related proteins at nerve-muscle junctions. Neuro. Report. 1992;3:857–860. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

