Expression and function of alpha(v)beta(3) and alpha(v)beta(5) integrins in the developing pancreas: roles in the adhesion and migration of putative endocrine progenitor cells
- PMID: 10995448
- PMCID: PMC2150716
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.150.6.1445
Expression and function of alpha(v)beta(3) and alpha(v)beta(5) integrins in the developing pancreas: roles in the adhesion and migration of putative endocrine progenitor cells
Abstract
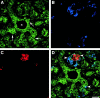
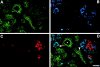
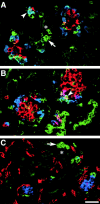
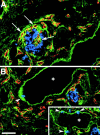
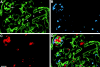
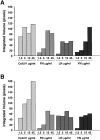
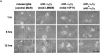
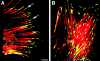
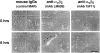
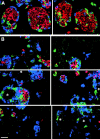
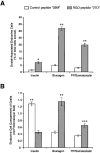
Cell-cell and cell-matrix interactions play a critical role in tissue morphogenesis and in homeostasis of adult tissues. The integrin family of adhesion receptors regulates cellular interactions with the extracellular matrix, which provides three-dimensional information for tissue organization. It is currently thought that pancreatic islet cells develop from undifferentiated progenitors residing within the ductal epithelium of the fetal pancreas. This process involves cell budding from the duct, migration into the surrounding mesenchyme, differentiation, and clustering into the highly organized islet of Langerhans. Here we report that alpha(v)beta(3) and alpha(v)beta(5), two integrins known to coordinate epithelial cell adhesion and movement, are expressed in pancreatic ductal cells and clusters of undifferentiated cells emerging from the ductal epithelium. We show that expression and function of alpha(v)beta(3) and alpha(v)beta(5) integrins are developmentally regulated during pancreatic islet ontogeny, and mediate adhesion and migration of putative endocrine progenitor cells both in vitro and in vivo in a model of pancreatic islet development. Moreover, we demonstrate the expression of fibronectin and collagen IV in the basal membrane of pancreatic ducts and of cell clusters budding from the ductal epithelium. Conversely, expression of vitronectin marks a population of epithelial cells adjacent to, or emerging from, pancreatic ducts. Thus, these data provide the first evidence for the contribution of integrins alpha(v)beta(3) and alpha(v)beta(5) and their ligands to morphogenetic events in the human endocrine pancreas.
Figures


References
-
- Alpert S., Hanahan D., Tietelman G. Hybrid insulin gene reveal a developmental lineage for pancreatic endocrine cell and imply a relationship with neurons. Cell. 1988;53:295–308. - PubMed
-
- Bauer G.E., Balsamo J., Lilien J. Cadherin-mediated adhesion in pancreatic islet cells is modulated by a cell surface N-acetylgalactosaminylphosphotransferase. J. Cell Sci. 1992;103:1235–1241. - PubMed
-
- Beattie G.M., Levine F., Mally M.I., Otonkoski T., O'Brien J.S., Salomon D.R., Hayek A. Acid β-galactosidasea developmentally regulated marker of endocrine cell precursors in the human fetal pancreas. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1994;78:1232–1240. - PubMed
-
- Beattie G.M., Rubin J.S., Mally M.I., Otonkoski T., Hayek A. Regulation of proliferation and differentiation of human fetal pancreatic islet cells by extracellular matrix, hepatocyte growth factor and cell-cell contact. Diabetes. 1996;45:1223–1228. - PubMed
-
- Beattie G.M., Cirulli V., Lopez A.D., Hayek A. Ex vivo expansion of human pancreatic endocrine cells. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1997;82:1852–1856. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

