How WASP regulates actin polymerization
- PMID: 10995455
- PMCID: PMC2150696
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.150.6.f117
How WASP regulates actin polymerization
Figures
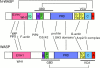
Comment on
-
Mechanism of N-WASP activation by CDC42 and phosphatidylinositol 4, 5-bisphosphate.J Cell Biol. 2000 Sep 18;150(6):1299-310. doi: 10.1083/jcb.150.6.1299. J Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 10995436 Free PMC article.
-
Activation by Cdc42 and PIP(2) of Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein (WASp) stimulates actin nucleation by Arp2/3 complex.J Cell Biol. 2000 Sep 18;150(6):1311-20. doi: 10.1083/jcb.150.6.1311. J Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 10995437 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brunnell S.C.P., Henry A., Kolluri R., Kirchhausen T., Rickles R.J., Berg L.J. Identification of Itk/Tsk src homology 3 domain ligands. J. Biol. Chem. 1996;271:25646–25656. - PubMed
-
- Carlier M-F., Nioche P., Broutin-L'Hermite I., Boujemaa R., Le Clainche C., Egile C., Garbay C., Ducruix A., Sansonetti P., Pantaloni D. Grb2 links signalling to actin assembly by enhancing interaction of neural Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein (N-WASP) with actin-related proteins (Arp2/3) complex. J. Biol. Chem. 2000;275:21969–21974. - PubMed
-
- Castellano F., Montcourrier P., Guillemot J-C., Guin E., Machesky L., Cossart P., Chavrier P. Inducible recruitment of Cdc42 or WASP to a cell-surface receptor triggers actin polymerization and filopodium formation. Curr. Biol. 1999;9:351–360. - PubMed
-
- Chen F., Ma L., Parrini M.C., Mao X., Lopez M., Wu C., Marks P.W., Davidson L., Kwiatkowski D.J., Kirchhausen T. Cdc42 is required for PIP2-induced actin polymerization and early development but not for cell viability. Curr. Biol. 2000;10:758–765. - PubMed

