Interactions between immune and bone cells: new insights with many remaining questions
- PMID: 10995785
- PMCID: PMC381401
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI11089
Interactions between immune and bone cells: new insights with many remaining questions
Figures
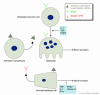
Comment on
-
Functional human T-cell immunity and osteoprotegerin ligand control alveolar bone destruction in periodontal infection.J Clin Invest. 2000 Sep;106(6):R59-67. doi: 10.1172/jci10763. J Clin Invest. 2000. PMID: 10995794 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Prockop DJ. Marrow stromal cells as stem cells for nonhematopoietic tissues. Science. 1997;276:71–74. - PubMed
-
- Horton JE, Raisz LG, Simmons HA, Oppenheim JJ, Mergenhagen SE. Bone resorbing activity in supernatant fluid from cultured human peripheral blood leukocytes. Science. 1972;177:793–795. - PubMed
-
- Dewhirst FE, Stashenko PP, Mole JE, Tsurumachi T. Purification and partial sequence of human osteoclast-activating factor: identity with interleukin 1 beta. J Immunol. 1985;135:2562–2568. - PubMed
-
- Bertolini DR, Nedwin GE, Bringman TS, Smith DD, Mundy GR. Stimulation of bone resorption and inhibition of bone formation in vitro by human tumour necrosis factors. Nature. 1986;319:516–518. - PubMed
-
- Ishimi Y, et al. IL-6 is produced by osteoblasts and induces bone resorption. J Immunol. 1990;145:3297–3303. - PubMed

