Efficacy of postexposure prophylaxis after intravaginal exposure of pig-tailed macaques to a human-derived retrovirus (human immunodeficiency virus type 2)
- PMID: 11000253
- PMCID: PMC112413
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.74.20.9771-9775.2000
Efficacy of postexposure prophylaxis after intravaginal exposure of pig-tailed macaques to a human-derived retrovirus (human immunodeficiency virus type 2)
Abstract
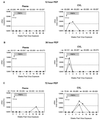
Postexposure prophylaxis (PEP) after intravaginal exposure to human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) was investigated using the HIV type 2 (HIV-2)/pig-tailed macaque transmission model. PEP for 28 days with the reverse transcriptase inhibitor (R)-9-(2-phosphonylmethoxypropyl)adenine (PMPA; tenofovir) was initiated 12 to 72 h following HIV-2 exposure. Systemic infection was not evident in the 12- and 36-h groups, as defined by plasma viremia, cell-associated provirus, antibody responses, and lymph node virus. Breakthrough infection in the 72-h group was detected at week 16 post-virus exposure. These results demonstrate for the first time using a vaginal transmission model that early intervention after high-risk sexual exposures may prevent infection.
Figures
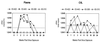
Similar articles
-
Antiretroviral therapy during primary immunodeficiency virus infection can induce persistent suppression of virus load and protection from heterologous challenge in rhesus macaques.J Virol. 2000 Feb;74(4):1704-11. doi: 10.1128/jvi.74.4.1704-1711.2000. J Virol. 2000. PMID: 10644340 Free PMC article.
-
Administration of 9-[2-(phosphonomethoxy)propyl]adenine (PMPA) for prevention of perinatal simian immunodeficiency virus infection in rhesus macaques.AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1998 Jun 10;14(9):761-73. doi: 10.1089/aid.1998.14.761. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1998. PMID: 9643376
-
Effect of PMPA and PMEA on the kinetics of viral load in simian immunodeficiency virus-infected macaques.AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2000 May 20;16(8):791-800. doi: 10.1089/088922200308783. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2000. PMID: 10826485
-
Tenofovir-related nephrotoxicity: case report and review of the literature.Pharmacotherapy. 2004 Mar;24(3):415-8. doi: 10.1592/phco.24.4.415.33182. Pharmacotherapy. 2004. PMID: 15040657 Review.
-
Acyclic nucleoside phosphonates in the chemotherapy of DNA virus and retrovirus infections.Intervirology. 1997;40(5-6):295-303. doi: 10.1159/000150563. Intervirology. 1997. PMID: 9675635 Review.
Cited by
-
A drug evaluation of 1% tenofovir gel and tenofovir disoproxil fumarate tablets for the prevention of HIV infection.Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2012 May;21(5):695-715. doi: 10.1517/13543784.2012.667072. Epub 2012 Mar 7. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2012. PMID: 22394224 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Does antiretroviral therapy prevent HIV transmission to sexual partners?Curr Infect Dis Rep. 2008 May;10(2):140-5. doi: 10.1007/s11908-008-0025-8. Curr Infect Dis Rep. 2008. PMID: 18462589
-
Awareness and low uptake of post exposure prophylaxis for HIV among clinical medical students in a high endemicity setting.BMC Public Health. 2015 Nov 6;15:1104. doi: 10.1186/s12889-015-2468-9. BMC Public Health. 2015. PMID: 26545721 Free PMC article.
-
Biomedical Interventions for HIV Prevention and Control: Beyond Vaccination.Viruses. 2025 May 26;17(6):756. doi: 10.3390/v17060756. Viruses. 2025. PMID: 40573348 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Use of non-occupational post-exposure prophylaxis does not lead to an increase in high risk sex behaviors in men who have sex with men participating in the EXPLORE trial.AIDS Behav. 2010 Oct;14(5):1182-9. doi: 10.1007/s10461-010-9712-1. AIDS Behav. 2010. PMID: 20490908 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Black R J. Animal studies of prophylaxis. Am J Med. 1997;102:39–44. - PubMed
-
- Böttiger D, Johansson N-G, Samuelsson B, Zhang H, Putkonen P, Vrang L, Öberg B. Prevention of simian immunodeficiency virus, SIVsm, or HIV-2 infection in cynomolgus monkeys by pre- and postexposure administration of BEA-005. AIDS. 1997;11:157–162. - PubMed
-
- Cardo D M, Culver D H, Ciesielski C A, Srivastava P U, Marcus R, Abiteboul D, Heptonstall J, Ippolito G, Lot F, McKibben P S, Bell D M the CDC Needlestick Surveillance Group. A case-control study of HIV seroconversation in health care workers after percutaneous exposure. N Engl J Med. 1997;337:1485–1490. - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Case control study of HIV seroconversation in health-care workers after percutaneous exposure to HIV-infected blood—France, United Kingdom, and United States, January 1988–August 1994. Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 1995;44:929–933. - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Management of possible sexual, injecting-drug-use, or other nonoccupational exposure to HIV, including considerations related to antiretroviral therapy: Public Health Service statement. Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 1998;47(RR17):1–14. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

