A novel AP-1 element in the CD95 ligand promoter is required for induction of apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells upon treatment with anticancer drugs
- PMID: 11003676
- PMCID: PMC86378
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.20.20.7826-7837.2000
A novel AP-1 element in the CD95 ligand promoter is required for induction of apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells upon treatment with anticancer drugs
Abstract
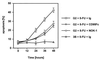
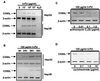
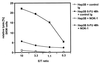
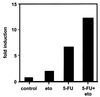
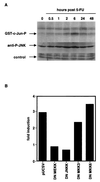
The CD95 (also called APO-1 or Fas) system plays a major role in the induction of apoptosis in lymphoid and nonlymphoid tissues in response to a variety of extracellular signals, including chemotherapeutic drugs. Here we report that the CD95 ligand (CD95L) is upregulated in hepatoma cells upon treatment with antineoplastic drugs. Upregulation by different chemotherapeutic drugs is functionally relevant for drug-induced apoptosis and is mediated by transcriptional mechanisms. The MEKK1/JNKK pathway and a novel AP-1 element in the CD95L promoter downstream of the TATA box are required for CD95L upregulation. Thus, understanding the mechanisms of CD95-mediated apoptosis through CD95L upregulation upon treatment of hepatocellular carcinomas with chemotherapeutic drugs may contribute to the improvement of anticancer chemotherapy.
Figures
References
-
- Angel P, Allegretto E A, Okino S T, Hattori K, Boyle W J, Hunter T, Karin M. Oncogene jun encodes a sequence-specific trans-activator similar to AP-1. Nature. 1988;332:166–171. - PubMed
-
- Angel P, Hattori K, Smeal T, Karin M. The jun proto-oncogene is positively autoregulated by its product, Jun/AP-1. Cell. 1988;55:875–885. - PubMed
-
- Behrens A, Sibilia M, Wagner E F. Amino-terminal phosphorylation of c-Jun regulates stress-induced apoptosis and cellular proliferation. Nat Genet. 1999;21:326–329. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
