Attenuation of sepsis-induced apoptosis by heat shock pretreatment in rats
- PMID: 11005377
- PMCID: PMC312885
- DOI: 10.1379/1466-1268(2000)005<0188:aosiab>2.0.co;2
Attenuation of sepsis-induced apoptosis by heat shock pretreatment in rats
Abstract
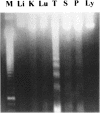
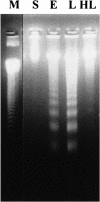
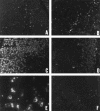
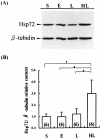
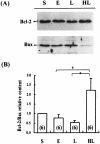
Apoptosis is a process by which cells undergo a form of non-necrotic cellular suicide. Although it is a programmed process, apoptosis can be induced by various stressors. During sepsis, apoptosis has been regarded as an important cause of cell death in the immune system, leading to unresponsiveness to treatment. This study was designed to investigate how prior heat shock induction can influence the rate of apoptosis in animals that have experienced sepsis. Sprague-Dawley rats were used, and experimental sepsis was induced by cecal ligation and puncture (CLP). Animals in the heated group were anesthetized and received heat shock by whole-body hyperthermia. They were sacrificed 9 h and 18 h after CLP as early and late sepsis, respectively. Apoptosis was evaluated by "DNA ladder" detection in agarose electrophoresis and Tdt-mediated dUTP nick end-labeling (TUNEL) assay. Hsp72 was detected by Western blot analysis. The results showed that the DNA ladder was detected most clearly in the thymus at the late phase of sepsis with time course dependence, while it showed less clearly in heat shock treated animals. Histopathological study by TUNEL assay obtained similar results in the thymus, where the cortex was more susceptible to apoptosis than the medulla. The Western blot analysis showed that the heat shock induced Hsp72 concomitant with an increase in Bcl-2:Bax ratio. In conclusion, heat shock pretreatment prevents rats from sepsis-induced apoptosis that may account for the better outcome of experimental sepsis. An increase in the Bcl-2:Bax ratio may in part explain the molecular mechanism of the effect of heat shock pretreatment.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The induction of heat shock protein-72 attenuates cisplatin-induced acute renal failure in rats.Pflugers Arch. 2003 Apr;446(1):116-24. doi: 10.1007/s00424-002-0996-5. Epub 2003 Feb 15. Pflugers Arch. 2003. PMID: 12690470
-
Potential protective effect of NF-kappaB activity on the polymicrobial sepsis of rats preconditioning heat shock treatment.Clin Chim Acta. 2000 Dec;302(1-2):11-22. doi: 10.1016/s0009-8981(00)00334-x. Clin Chim Acta. 2000. PMID: 11074060
-
Heat shock pretreatment prevents cardiac mitochondrial dysfunction during sepsis.Shock. 2003 Sep;20(3):274-9. doi: 10.1097/00024382-200309000-00013. Shock. 2003. PMID: 12923501
-
'Heated' debates in apoptosis.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2007 Sep;64(18):2329-33. doi: 10.1007/s00018-007-7135-6. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2007. PMID: 17572850 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Apoptosis.Crit Care Med. 2005 Dec;33(12 Suppl):S526-9. doi: 10.1097/01.ccm.0000185499.28006.4c. Crit Care Med. 2005. PMID: 16340441 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Role of Exogenous Hsp72 on Liver Dysfunction during Sepsis.Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:508101. doi: 10.1155/2015/508101. Epub 2015 Jun 29. Biomed Res Int. 2015. PMID: 26221596 Free PMC article.
-
The induction of heat shock protein-72 attenuates cisplatin-induced acute renal failure in rats.Pflugers Arch. 2003 Apr;446(1):116-24. doi: 10.1007/s00424-002-0996-5. Epub 2003 Feb 15. Pflugers Arch. 2003. PMID: 12690470
-
Does hyperthermic preconditioning affect the rate of surgical site infection rate and inflammatory reaction in colorectal cancer patients? A prospective randomized clinical trial.Turk J Surg. 2018 Sep 11;34(4):282-285. doi: 10.5152/turkjsurg.2018.3981. Turk J Surg. 2018. PMID: 30248285 Free PMC article.
-
Sepsis: prognostic role of apoptosis regulators in gastrointestinal cells.World J Surg. 2007 Apr;31(4):787-94. doi: 10.1007/s00268-005-0742-1. World J Surg. 2007. PMID: 17372670
-
Heat-shock response protects peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) from hydrogen peroxide-induced mitochondrial disturbance.Cell Stress Chaperones. 2009 Mar;14(2):207-17. doi: 10.1007/s12192-008-0075-8. Epub 2008 Sep 2. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2009. PMID: 18763057 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ayala A, Herdon CD, Lehman DL, Ayala CA, Chaudry IH. Differential induction of apoptosis in lymphoid tissues during sepsis: variation in onset, frequency, and the nature of the mediators. Blood. 1996;87:4261–4275. - PubMed
-
- Ayala A, Herdon CD, Lehman DL, DeMaso CM, Ayala CA, Chaudry IH. The induction of accelerated thymic programmed cell death during polymicrobial sepsis: control by corticosteroids but not tumor necrosis factor. Shock. 1995;3:259–267. - PubMed
-
- Buzzard KA, Giaccia AJ, Killender M, Anderson RL. Heat shock protein 72 modulates pathway of stress-induced apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:17147–17153. - PubMed
-
- Chao DT, Korsmeyer SJ. Bcl-2 family: regulators of cell death. Annu Rev Immunol. 1998;16:395–419. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
