Aryl hydrocarbon (Ah) receptor levels are selectively modulated by hsp90-associated immunophilin homolog XAP2
- PMID: 11005382
- PMCID: PMC312890
- DOI: 10.1379/1466-1268(2000)005<0243:aharla>2.0.co;2
Aryl hydrocarbon (Ah) receptor levels are selectively modulated by hsp90-associated immunophilin homolog XAP2
Abstract
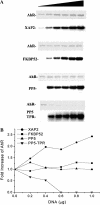
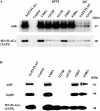
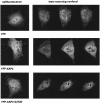
The aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) is a ligand-inducible transcription factor that mediates biological responses to halogenated aromatic hydrocarbons. The unliganded AhR is a cytoplasmic, tetrameric complex consisting of the AhR ligand-binding subunit, a dimer of hsp90, and the hepatitis B virus X-associated protein 2 (XAP2). The role of XAP2 as a member of the AhR core complex is poorly understood. XAP2 shares significant homology with the immunophilins FKBP12 and FKBP52, including a highly conserved, C-terminal, tetratricopeptide repeat (TPR) domain. XAP2 forms a complex with hsp90 and the AhR but can also bind to both independently. This binding is mediated by the conserved TPR domain. Single-point mutations in this region are sufficient to disrupt the association of XAP2 with both the AhR and hsp90 in cells. Cotransfection of the AhR and XAP2 in COS-1 cells results in increased AhR levels compared with cells transfected with the AhR alone. In contrast, coexpression of the AhR with the TPR containing proteins FKBP52, protein phosphatase 5 (PP5), or XAP2 TPR-mutants deficient in binding to the AhR and hsp90 does not affect AhR levels and coexpression of the AhR with the TPR domain of PP5 results in AhR down-regulation. These results demonstrate that XAP2 is apparently unique among hsp90-binding proteins in its ability to enhance AhR levels. A yellow fluorescent protein (YFP)-XAP2-FLAG was constructed and biochemically characterized, and no loss of function was detected. YFP-XAP2-FLAG was transiently transfected into NIH 3T3 and was found to localize in both the nucleus and the cytoplasm when visualized by fluorescence microscopy. Treatment of Hepa-1 cells with the hsp90-binding benzoquinone ansamycin, geldanamycin, and the macrocyclic antifungal compound radicicol resulted in AhR but not XAP2 or FKBP52 turnover. Taken together, these results suggest that XAP2/hsp90 and FKBP52/hsp90 complexes are similar yet exhibit unique functional specificity.
Figures




References
-
- Barent RL, Nair SC, Carr DC, Ruan Y, Rimerman RA, Fulton J, Zhang Y, Smith DF. Analysis of FKBP51/FKBP52 chimeras and mutants for hsp90 binding and association with progesterone receptor complexes. Mol Endocrinol. 1998;12:342–354. - PubMed
-
- Bruner KL, Derfoul A, Robertson NM, Guerriero G, Fernandes-Alnemri T, Alnemri ES, Litwack G. The unliganded mineralocorticoid receptor is associated with heat shock proteins 70 and 90 and the immunophilin FKBP-52. Recept Signal Transduct. 1997;7:85–98. - PubMed
-
- Buchner J. Hsp90 & Co.—a holding for folding. TIBS. 1999;24:136–141. - PubMed
-
- Bukau B, Horwich AL. The Hsp70 and Hsp60 chaperone machines. Cell. 1998;92:351–366. - PubMed
-
- Carrello A, Ingley E, Minchin RF, Tsai S, Ratajczak T. The common tetratricopeptide repeat acceptor site for steroid receptor-associated immunophilins and Hop is located in the dimerization domain of Hsp90. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:2682–2689. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
