Induction of photosensitivity in neonatal rat pineal gland
- PMID: 11005846
- PMCID: PMC17236
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.210248297
Induction of photosensitivity in neonatal rat pineal gland
Abstract
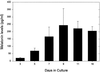
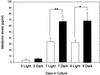
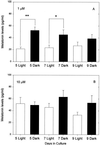
Pineal glands removed from neonatal rats at 5, 7, and 9 days of age and explanted into short-term culture, synthesized melatonin when stimulated with norepinephrine (NE); their melatonin synthesis could not be suppressed with bright white light. Dispersed pineal cell cultures or pineal explants prepared from 1-day-old neonates and held in culture for 7 or 9 days also synthesized melatonin when stimulated with NE, but in these cases melatonin synthesis was significantly suppressed by light, demonstrating that the pineals had become photosensitive while in culture. The development of photosensitivity in culture could be partially or completely abolished by the continuous presence of 1 or 10 microm of NE in the culture medium. The pineals of all nonmammalian vertebrates are photoreceptive, whereas those of mammals do not normally respond to light. We hypothesize that a mechanism to suppress pineal photosensitivity by using NE released from sympathetic nerve endings evolved early in the history of mammals.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Rhythmic melatonin response of the Syrian hamster pineal gland to norepinephrine in vitro and in vivo.J Pineal Res. 1986;3(3):235-49. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-079x.1986.tb00746.x. J Pineal Res. 1986. PMID: 3772722
-
Role of prostaglandins in rat pineal neuroeffector junction. Changes in melatonin and norepinephrine release in vitro.Endocrinology. 1982 Aug;111(2):530-4. doi: 10.1210/endo-111-2-530. Endocrinology. 1982. PMID: 6954068
-
Norepinephrine activates NF-κB transcription factor in cultured rat pineal gland.Life Sci. 2014 Jan 17;94(2):122-9. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2013.11.004. Epub 2013 Nov 14. Life Sci. 2014. PMID: 24239639
-
Cellular circadian clocks in the pineal.Prog Neurobiol. 1999 Jun;58(2):121-62. doi: 10.1016/s0301-0082(98)00078-1. Prog Neurobiol. 1999. PMID: 10338357 Review.
-
Evolution of melatonin-producing pinealocytes.Adv Exp Med Biol. 1999;460:17-29. doi: 10.1007/0-306-46814-x_3. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1999. PMID: 10810496 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Night/day changes in pineal expression of >600 genes: central role of adrenergic/cAMP signaling.J Biol Chem. 2009 Mar 20;284(12):7606-22. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M808394200. Epub 2008 Dec 22. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19103603 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of daily and circadian gene expression in the rat pineal gland.Neurosci Res. 2008 Feb;60(2):192-8. doi: 10.1016/j.neures.2007.10.011. Epub 2007 Nov 6. Neurosci Res. 2008. PMID: 18067983 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of novel opsins and intrinsic light responses in the mammalian retinal ganglion cell line RGC-5. Presence of OPN5 in the rat retina.PLoS One. 2011;6(10):e26417. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0026417. Epub 2011 Oct 17. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 22022612 Free PMC article.
-
Noradrenaline upregulates T-type calcium channels in rat pinealocytes.J Physiol. 2015 Feb 15;593(4):887-904. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2014.284208. Epub 2015 Jan 14. J Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25504572 Free PMC article.
-
Homeobox genes in the rodent pineal gland: roles in development and phenotype maintenance.Neurochem Res. 2013 Jun;38(6):1100-12. doi: 10.1007/s11064-012-0906-y. Epub 2012 Oct 18. Neurochem Res. 2013. PMID: 23076630 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Freedman M S, Lucas R J, Soni B, Von Schantz M, Munoz M, David-Gray Z, Foster R G. Science. 1999;284:502–504. - PubMed
-
- Menaker M, Tosini G. In: Circadian Organization and Oscillatory Coupling. Honma K, Honma S, editors. Sapporo, Japan: Hokkaido Univ. Press; 1996. pp. 39–52.
-
- Klein D C, Moore R Y, Reppert S M. Suprachiasmatic Nucleus: The Mind's Clock. New York: University Press; 1991.
-
- Torres G, Lytle L D. J Pineal Res. 1989;7:211–220. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

