UV radiation-sensitive norin 1 rice contains defective cyclobutane pyrimidine dimer photolyase
- PMID: 11006332
- PMCID: PMC149070
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.12.9.1569
UV radiation-sensitive norin 1 rice contains defective cyclobutane pyrimidine dimer photolyase
Abstract
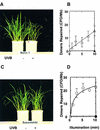
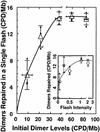
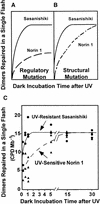
Norin 1, a progenitor of many economically important Japanese rice strains, is highly sensitive to the damaging effects of UVB radiation (wavelengths 290 to 320 nm). Norin 1 seedlings are deficient in photorepair of cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers. However, the molecular origin of this deficiency was not known and, because rice photolyase genes have not been cloned and sequenced, could not be determined by examining photolyase structural genes or upstream regulatory elements for mutations. We therefore used a photoflash approach, which showed that the deficiency in photorepair in vivo resulted from a functionally altered photolyase. These results were confirmed by studies with extracts, which showed that the Norin 1 photolyase-dimer complex was highly thermolabile relative to the wild-type Sasanishiki photolyase. This deficiency results from a structure/function alteration of photolyase rather than of nonspecific repair, photolytic, or regulatory elements. Thus, the molecular origin of this plant DNA repair deficiency, resulting from a spontaneously occurring mutation to UV radiation sensitivity, is defective photolyase.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Spontaneously occurring mutations in the cyclobutane pyrimidine dimer photolyase gene cause different sensitivities to ultraviolet-B in rice.Plant J. 2005 Jul;43(1):57-67. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2005.02428.x. Plant J. 2005. PMID: 15960616
-
Ultraviolet-B sensitivities in Japanese lowland rice cultivars: cyclobutane pyrimidine dimer photolyase activity and gene mutation.Plant Cell Physiol. 2004 Dec;45(12):1848-56. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pch215. Plant Cell Physiol. 2004. PMID: 15653803
-
Increase in CPD photolyase activity functions effectively to prevent growth inhibition caused by UVB radiation.Plant J. 2007 Apr;50(1):70-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2007.03041.x. Plant J. 2007. PMID: 17397507
-
All You Need Is Light. Photorepair of UV-Induced Pyrimidine Dimers.Genes (Basel). 2020 Nov 4;11(11):1304. doi: 10.3390/genes11111304. Genes (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33158066 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The photo repair of pyrimidine dimers by DNA photolyase and model systems.J Photochem Photobiol B. 1993 Mar;17(3):219-28. doi: 10.1016/1011-1344(93)80019-6. J Photochem Photobiol B. 1993. PMID: 8492239 Review.
Cited by
-
Integration and scaling of UV-B radiation effects on plants: from DNA to leaf.Ecol Evol. 2015 Jul;5(13):2544-55. doi: 10.1002/ece3.1332. Epub 2015 Jun 2. Ecol Evol. 2015. PMID: 26257869 Free PMC article.
-
Delimitation of the chromosomal region for a quantitative trait locus, qUVR- 10, conferring resistance to ultraviolet-B radiation in rice (Oryza sativa L.).Theor Appl Genet. 2004 Feb;108(3):385-91. doi: 10.1007/s00122-003-1460-4. Epub 2003 Nov 12. Theor Appl Genet. 2004. PMID: 14614563
-
Very high sensitivity of African rice to artificial ultraviolet-B radiation caused by genotype and quantity of cyclobutane pyrimidine dimer photolyase.Sci Rep. 2020 Feb 21;10(1):3158. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-59720-x. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32081870 Free PMC article.
-
The native cyclobutane pyrimidine dimer photolyase of rice is phosphorylated.Plant Physiol. 2008 Apr;146(4):1941-51. doi: 10.1104/pp.107.110189. Epub 2008 Jan 30. Plant Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18235036 Free PMC article.
-
qUVR-10, a major quantitative trait locus for ultraviolet-B resistance in rice, encodes cyclobutane pyrimidine dimer photolyase.Genetics. 2005 Dec;171(4):1941-50. doi: 10.1534/genetics.105.044735. Epub 2005 Jun 18. Genetics. 2005. PMID: 15965242 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bennett, P.V., Hada, M., Hidema, J., Lepre, A.M., Pope, L.C., Quaite, F.E., Sullivan, J.H., Takayanagi, S., Sutherland, J.C., and Sutherland, B.M. (2000). Isolation of high-molecular-length DNA: Alfalfa, pea, rice, sorghum, soybean, and spinach. Crop Sci., in press.
-
- Bornman, J.F., and Teramura, A.H. (1993). Effects of ultraviolet-B radiation on terrestrial plants. In Environmental UV Photobiology, A.R. Young, L.O. Bjorn, J. Moan, and W. Nultsch, eds (New York: Plenum Press), pp. 427–471.
-
- Britt, A.B. (1996). DNA damage and repair in plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant Mol. Biol. 47, 75–100. - PubMed
-
- Britt, A.B. (1999). Molecular genetics of DNA repair in higher plants. Trends Plant Sci. 4, 20–25. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

