Four genes of Medicago truncatula controlling components of a nod factor transduction pathway
- PMID: 11006338
- PMCID: PMC149076
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.12.9.1647
Four genes of Medicago truncatula controlling components of a nod factor transduction pathway
Abstract
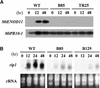
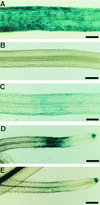
Rhizobium nodulation (Nod) factors are lipo-chitooligosaccharides that act as symbiotic signals, eliciting several key developmental responses in the roots of legume hosts. Using nodulation-defective mutants of Medicago truncatula, we have started to dissect the genetic control of Nod factor transduction. Mutants in four genes (DMI1, DMI2, DMI3, and NSP) were pleiotropically affected in Nod factor responses, indicating that these genes are required for a Nod factor-activated signal transduction pathway that leads to symbiotic responses such as root hair deformations, expressions of nodulin genes, and cortical cell divisions. Mutant analysis also provides evidence that Nod factors have a dual effect on the growth of root hair: inhibition of endogenous (plant) tip growth, and elicitation of a novel tip growth dependent on (bacterial) Nod factors. dmi1, dmi2, and dmi3 mutants are also unable to establish a symbiotic association with endomycorrhizal fungi, indicating that there are at least three common steps to nodulation and endomycorrhization in M. truncatula and providing further evidence for a common signaling pathway between nodulation and mycorrhization.
Figures

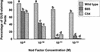


References
-
- Albrecht, C., Geurts, R., Lapeyrie, F., and Bisseling, T. (1998). Endomycorrhizae and rhizobial Nod factors both require Sym8 to induce the expression of the early nodulin genes PsENOD5 and PsENOD12A. Plant J. 15, 605–614. - PubMed
-
- Ardourel, M., Demont, N., Debellé, F., Maillet, F., de Billy, F., Promé, J.C., Dénarié, J., and Truchet, G. (1994). Rhizobium meliloti lipooligosaccharide nodulation factors: Different structural requirements for bacterial entry into target root hair cells and induction of plant symbiotic developmental responses. Plant Cell 6, 1357–1374. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Asad, S., Fang, Y.W., Wycoff, K.L., and Hirsch, A.M. (1994). Isolation and characterization of cDNA and genomic clones of MsENOD40: Transcripts are detected in meristematic cells of alfalfa. Protoplasma 183, 10–23.
-
- Barker, D.G., et al. (1990). Medicago truncatula, a model plant for studying the molecular genetics of the Rhizobium–legume symbiosis. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 8, 40–49.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

