Biogenesis of the chloroplast-encoded D1 protein: regulation of translation elongation, insertion, and assembly into photosystem II
- PMID: 11006346
- PMCID: PMC149084
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.12.9.1769
Biogenesis of the chloroplast-encoded D1 protein: regulation of translation elongation, insertion, and assembly into photosystem II
Abstract
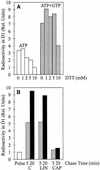
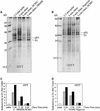
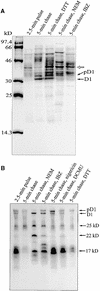
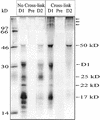
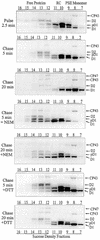
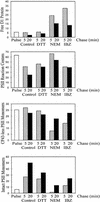
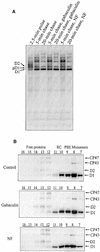
Regulation of translation elongation, membrane insertion, and assembly of the chloroplast-encoded D1 protein of photosystem II (PSII) was studied using a chloroplast translation system in organello. Translation elongation of D1 protein was found to be regulated by (1) a redox component that can be activated not only by photosynthetic electron transfer but also by reduction with DTT; (2) the trans-thylakoid proton gradient, which is absolutely required for elongation of D1 nascent chains on the thylakoid membrane; and (3) the thiol reactants N-ethylmaleimide (NEM) and iodosobenzoic acid (IBZ), which inhibit translation elongation with concomitant accumulation of distinct D1 pausing intermediates. These results demonstrate that D1 translation elongation and membrane insertion are tightly coupled and highly regulated processes in that proper insertion is a prerequisite for translation elongation of D1. Cotranslational and post-translational assembly steps of D1 into PSII reaction center and core complexes occurred independently of photosynthetic electron transfer or trans-thylakoid proton gradient but were strongly affected by the thiol reactants DTT, NEM, and IBZ. These compounds reduced the stability of the early PSII assembly intermediates, hampered the C-terminal processing of the precursor of D1, and prevented the post-translational reassociation of CP43, indicating a strong dependence of the D1 assembly steps on proper redox conditions and the formation of disulfide bonds.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Kinetic resolution of the incorporation of the D1 protein into photosystem II and localization of assembly intermediates in thylakoid membranes of spinach chloroplasts.J Biol Chem. 1996 Apr 19;271(16):9627-36. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.16.9627. J Biol Chem. 1996. PMID: 8621638
-
In vitro synthesis and assembly of photosystem II core proteins. The D1 protein can be incorporated into photosystem II in isolated chloroplasts and thylakoids.J Biol Chem. 1995 Oct 27;270(43):25685-95. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.43.25685. J Biol Chem. 1995. PMID: 7592747
-
A SecY homologue is involved in chloroplast-encoded D1 protein biogenesis.J Biol Chem. 2001 Oct 12;276(41):37809-14. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M105522200. Epub 2001 Jul 25. J Biol Chem. 2001. PMID: 11473124
-
Synthesis, membrane insertion and assembly of the chloroplast-encoded D1 protein into photosystem II.FEBS Lett. 2002 Feb 13;512(1-3):13-8. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(02)02218-4. FEBS Lett. 2002. PMID: 11852043 Review.
-
Chloroplast translation regulation.Photosynth Res. 2007 Nov-Dec;94(2-3):359-74. doi: 10.1007/s11120-007-9183-z. Epub 2007 Jul 28. Photosynth Res. 2007. PMID: 17661159 Review.
Cited by
-
Mutagenesis of a light-regulated psbA intron reveals the importance of efficient splicing for photosynthetic growth.Nucleic Acids Res. 2003 Aug 1;31(15):4361-72. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkg643. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003. PMID: 12888495 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of translation by the redox state of elongation factor G in the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803.J Biol Chem. 2009 Jul 10;284(28):18685-91. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.015131. Epub 2009 May 15. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19447882 Free PMC article.
-
Experimental approaches to studying translation in plant semi-autonomous organelles.J Exp Bot. 2024 Sep 11;75(17):5175-5187. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erae151. J Exp Bot. 2024. PMID: 38592734 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Systematic analysis of the relation of electron transport and ATP synthesis to the photodamage and repair of photosystem II in Synechocystis.Plant Physiol. 2005 Jan;137(1):263-73. doi: 10.1104/pp.104.054478. Epub 2004 Dec 23. Plant Physiol. 2005. PMID: 15618415 Free PMC article.
-
Ribosome nascent chain complexes of the chloroplast-encoded cytochrome b6 thylakoid membrane protein interact with cpSRP54 but not with cpSecY.J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2015 Jun;47(3):265-78. doi: 10.1007/s10863-014-9598-0. Epub 2015 Jan 6. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2015. PMID: 25561393 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adir, N., Shochat, S., and Ohad, I. (1990). Light-dependent D1 protein synthesis and translocation is regulated by reaction center II: Reaction center II serves as an acceptor for the D1 precursor. J. Biol. Chem. 265, 12563–12568. - PubMed
-
- Aro, E.-M., Virgin, I., and Andersson, B. (1993). Photoinhibition of photosystem II. Inactivation, protein damage and turnover. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1143, 113–143. - PubMed
-
- Baena-Gonzalez, E., Barbato, R., and Aro, E.-M. (1999). Role of phosphorylation in the repair cycle and oligomeric structure of photosystem II. Planta 208, 196–204.
-
- Bowyer, J.R., Packer, J.C.L., McCormack, B.A., Whitelegge, J.P., Robinson, C., and Tayor, M. (1992). Carboxyl-terminal processing of the D1 protein and photoactivation of water splitting in photosystem II. J. Biol. Chem. 267, 5424–5433. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

