Enhanced proliferation, survival, and dopaminergic differentiation of CNS precursors in lowered oxygen
- PMID: 11007896
- PMCID: PMC6772777
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.20-19-07377.2000
Enhanced proliferation, survival, and dopaminergic differentiation of CNS precursors in lowered oxygen
Abstract
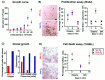
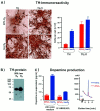
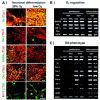
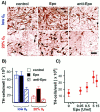
Standard cell culture systems impose environmental oxygen (O(2)) levels of 20%, whereas actual tissue O(2) levels in both developing and adult brain are an order of magnitude lower. To address whether proliferation and differentiation of CNS precursors in vitro are influenced by the O(2) environment, we analyzed embryonic day 12 rat mesencephalic precursor cells in traditional cultures with 20% O(2) and in lowered O(2) (3 +/- 2%). Proliferation was promoted and apoptosis was reduced when cells were grown in lowered O(2), yielding greater numbers of precursors. The differentiation of precursor cells into neurons with specific neurotransmitter phenotypes was also significantly altered. The percentage of neurons of dopaminergic phenotype increased to 56% in lowered O(2) compared with 18% in 20% O(2). Together, the increases in total cell number and percentage of dopaminergic neurons resulted in a ninefold net increase in dopamine neuron yield. Differential gene expression analysis revealed more abundant messages for FGF8, engrailed-1, and erythropoietin in lowered O(2). Erythropoietin supplementation of 20% O(2) cultures partially mimicked increased dopaminergic differentiation characteristic of CNS precursors cultured in lowered O(2). These data demonstrate increased proliferation, reduced cell death, and enhanced dopamine neuron generation in lowered O(2), making this method an important advance in the ex vivo generation of specific neurons for brain repair.
Figures
References
-
- Bany-Mohammed FM, Slivka S, Hallman M. Recombinant human erythropoietin: possible role as an antioxidant in premature rabbits. Pediatr Res. 1996;40:381–387. - PubMed
-
- Colton DA, Pagan F, Snell J, Colton JS, Cummins A, Gilbert DL. Protection from oxidation enhances the survival of cultured mesencephalic neurons. Exp Neurol. 1995;132:54–61. - PubMed
-
- Czyzyk-Krzeska MF, Furnari BA, Lawson EE, Millhorn DE. Hypoxia increases rate of transcription and stability of tyrosine hydroxylase mRNA in pheochromocytoma (PC12) cells. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:760–764. - PubMed
-
- Danelian PS, McMahon AP. Engrailed-1 as a target of the Wnt-1 signalling pathway in vertebrate midbrain development. Nature. 1996;383:332–334. - PubMed
-
- Echelard Y, Epstein DJ, St-Jacques B, Shen L, Mahler J, McMahon JA, McMahon AP. Sonic hedgehog, a member of a family of putative signaling molecules, is implicated in the regulation of CNS polarity. Cell. 1993;75:1417–1430. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
